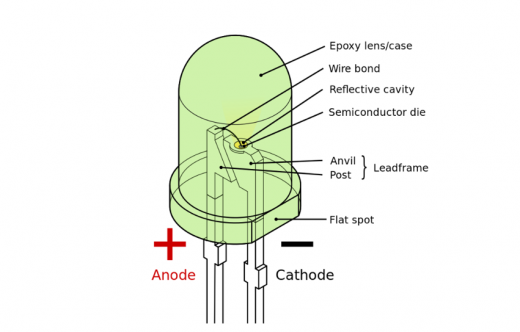
What is LED
The full name of LED is light-emitting diode, or energy-saving lamp for short. The LED’s high efficiency, energy saving and environmental protection and other factors quickly replaced the previous incandescent lamp. It is difficult to see the previous incandescent lamp on the market now, and the domestic and commercialization of LED is becoming more and more common, or such a magical energy-saving lamp that illuminates the earth, how does it shine? What kind of light can it emit?
In fact, the core device of LED is what we usually call semiconductor.
Classification of Semiconductors
After understanding the structure of LED, we will focus on the core part of LED-semiconductor. Semiconductors, as the name suggests, are half conductive and the other half non-conductive, but this is not very appropriate. It can be understood that the conductivity is between the conductor and the insulator. In addition, semiconductors can be divided into P-type and N-type semiconductors. The difference between P-type and N-type semiconductors is that they are doped differently.
Semiconductors contain minority “holes” (holes do not actually exist, but a kind of virtual particles, which are positively charged) and multiple “electrons (negatively charged)”. Generally speaking, the minority carrier “holes” contained in P-type semiconductors are more than that of multi-carrier electrons, while the multi-carrier electrons in N-type semiconductors are more than the minority “holes”.
Why Can LED Emit Light
When we apply voltage to the two semiconductors, the electrons in one semiconductor run out under the action of the electric field, and the holes in the other semiconductor run out under the action of the electric field. When the holes and electrons When the gaps between the bulk semiconductors meet, an “electron-hole pair” annihilation phenomenon occurs, that is, the “electron- hole pair” disappears.
According to the law of conservation of energy and momentum, it is transformed into a photon pair, and other forms of energy (such as heat) may be released at the same time. The reason why we can see that the LED can emit light after applying a certain voltage is because of the annihilation effect of the “electron-hole pair” in the semiconductor.
How many kinds of light can LED emit?
Semiconductors have energy band structures, and different semiconductors have different energy band structures. In theory, we can always find some ideal materials to enable LEDs to emit light of different colors, but in fact, due to material limitations, we can only make LEDs emit light in a limited number of colors. In 2015, the Nobel Prize was awarded to Shuji Nakamura in Japan for their outstanding contributions to high-efficiency blue LEDs. It can be seen that it is difficult enough to make blue LEDs emit light because they can emit blue LEDs. Optical semiconductor materials are difficult to synthesize.
With the rapid development of physics and corresponding disciplines, more and more efficient, inexpensive, and energy-saving multi-color LEDs will be effectively developed.
LED chip Technology and Application Design
Compared with traditional light sources such as incandescent lamps and compact fluorescent lamps, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have many advantages such as high luminous efficiency, long life, and high directivity. They are increasingly favored by the industry and are used in the general lighting (General Lighting) market.
In order to accelerate the popularization of LED lighting applications, there are still problems from cost, technology, and standards that must be overcome in the short term. Technical aspects, including color temperature, color rendering, and efficiency improvement, still need to be further improved. The application of LEDs in the general lighting market involves many requirements, which must be considered from a system perspective, such as LED light source, power conversion, drive control, heat dissipation, and optics.
Thin film chip technology shows its edge
At present, the key to the development of LED chip technology lies in substrate materials and wafer growth technology. In addition to the traditional sapphire materials, silicon (Si), and silicon carbide (SiC) as the base material, zinc oxide (ZnO) and gallium nitride (GaN) are also the focus of current research. Whether it is high-power chips for key lighting and overall lighting, or low-power chips for decorative lighting and some simple auxiliary lighting, the key to technological improvement is how to develop more efficient and stable chips.
Therefore, improving the efficiency of LED chips becomes the key to improving the overall technical indicators of LED lighting. In just a few years, with the help of a series of technological improvements such as chip structure, surface roughening, and multiple quantum well structure design, LEDs have made major breakthroughs in luminous efficiency. It is believed that as the technology continues to mature, LED quantum efficiency will be further improved, and the luminous efficiency of LED chips will also increase.
Thinfilm technology is the key technology for producing super bright LED chips, which can reduce the lateral light loss. Through the bottom reflective surface, more than 97% of the light can be output from the front, which not only greatly improves the LED luminous efficiency, but also the lens design It’s easier.
Advantages of LED Light Source
The life span of lamps has always been one of the main issues that everyone is concerned about. To build a good heat dissipation system for lamps, it is not enough to select LED components with low thermal resistance. The thermal resistance from the PN junction to the environment must be effectively reduced to reduce the PN junction temperature of the LED as much as possible, and to increase the life of the LED lamp and the actual luminous flux .
Different from traditional light sources, PCB is the power supply carrier of LED, and also the heat dissipation carrier. Therefore, the heat dissipation design of PCB and heat sink is also particularly important. In addition, the material, thickness, area size of the heat dissipation material, the treatment of the heat dissipation interface, and the connection method are all factors that the lamp manufacturer must consider.
Optical design should make good use of LED standards
The directionality and point light source of LED are one of the most typical characteristics different from traditional light sources. How to use these two characteristics of LED is the key to the optical design of lamps. Through the secondary optical design of LEDs, LED lamps can achieve a relatively ideal light distribution curve.
For example, in the overall indoor lighting, the brightness of the lamps is required to be high, and a lampshade with higher transmittance can be used to improve the light extraction efficiency; there are also lamps The light guide plate technology is added to make the LED point light source become a surface light source to improve its uniformity and prevent glare.
In addition, some auxiliary lighting and accent lighting require a certain light-gathering effect to highlight the illuminated object, and you can choose to match some light-gathering Lens or reflector to meet optical requirements.
Driver design must ensure constant current output
The requirement of LED for the drive circuit is to ensure constant current output. When the LED is working in the forward direction, the relative change area of the LED forward voltage is small. To ensure the constant LED drive current is to ensure the constant output power of the LED. In addition, the dimming design is also one of the mainstream designs of the current driving circuit.
This is more used in some scene lighting. Different brightness can be adjusted according to different environments to fully achieve energy-saving effects. At present, the main design direction of the driver revolves around improving the power factor of the power supply, reducing the power consumption, improving the control accuracy and speeding up the response speed.
In addition to the design of the drive power supply, PCB wiring and series-parallel connection are also considerations.
Indispensable for standard setting
As a brand-new field, LED lighting requires the formulation of product standards, measurement standards, control and interface standards, etc. In addition, the current LED lighting products on the market are uneven, and many product information is not complete, which can easily mislead consumers.
Including the competition between organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) and other high-efficiency light sources and traditional low-cost light sources, the LED lighting industry urgently needs a complete standard system to maintain and promote the healthy and sustainable development of the industry. At present, the US Department of Energy (DOE) is actively promoting related standards for semiconductor lighting, and China, Taiwan Province, South Korea, Japan, etc. are also actively developing LED standards.
Get rid of phosphors restrict low color temperature luminous efficiency
Indoor home lighting tends to tend to a low color temperature below 4000K. Warm white light makes the whole environment more warm and relaxing; while cold white light gives people a clean, efficient and bright feeling, suitable for office lighting and outdoor lighting. Affected by phosphors, the luminous efficiency of LEDs at low color temperatures is often about 30% lower than that at high color temperatures.
Hybrid red LED takes into account light efficiency and color rendering index
The higher the luminous efficiency of the LED, the color rendering index is often somewhat low, and indoor lighting requires that the brightness and color of the object can be objectively displayed to obtain the real effect of direct observation of the external scenery by the human eye, so higher color rendering is usually required index. This requires the LED to further increase the color rendering index while increasing the luminous efficiency, but it is also possible to mix some red LEDs at the lamp level to obtain the effect of a display index greater than 90.
Improve high-current drive efficiency and reduce LED costs
At this stage, the driving current of 1 watt LED can reach 350 to 1,000 mA, but usually under high current driving conditions, although the luminous flux increases, the overall efficiency drops significantly, so there is a gap between the overall cost and the system luminous efficiency It is necessary to find a balance. If the luminous efficiency of LEDs under high-current driving can be improved, the number of LEDs required can be greatly reduced under the premise of higher system luminous efficiency, thereby significantly reducing costs.
Reducing the package size of the LED helps increase design flexibility
Under the premise of energy saving, environmental protection and health, the development of LED indoor lamps and lanterns will also develop in the direction of art, miniaturization and individualization. Therefore, reducing the package size of LEDs can increase the flexibility and innovation space in lamp design. In some occasions where light mixing must be used to improve color rendering, a smaller package size will facilitate the design of the light mixing lens and the effect of light mixing.