The measurement of light, especially the measurement of the spectrum, has become particularly important in the LED era. Whether it is manufacturer R&D personnel, technical and sales personnel, or designers and owners, measuring and understanding the spectral composition of lamps and lanterns is already a must.
1. Radiation Measurement
Radiometry is the science of measuring electromagnetic radiation over a spectrum based on physical constants. The radiation properties we are concerned with are the radiated power and its distribution in space and angle.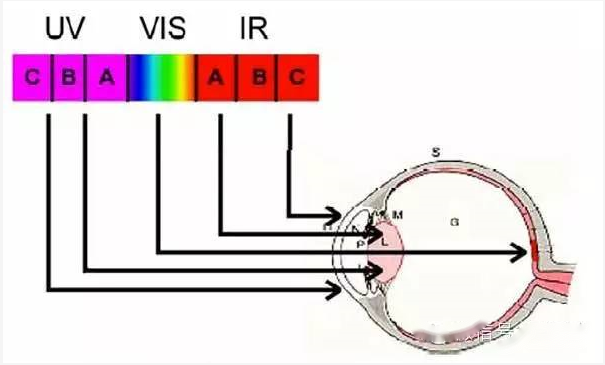
Figure: Penetration of optical radiation to the human eye.
First of all, it is necessary to clarify the four basic concepts of radiant flux, radiant intensity, radiance and radiance.
1.1 Radiant flux
This is the transmit power emitted by the source or received by the surface. It can also be defined as the rate at which energy is radiated through a specific area or solid angle.
The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt.
1.2 Radiation intensity
It is defined as the radiation density within a certain angle from the source. The radiant intensity in a particular direction is the sum of the power (eg power per solid angle) of all the radiation emitted by the entire light source in that direction (cone-shaped).
The SI unit of radiation intensity is watts/steradian (Watt/sr).
1.3 Irradiance
This is a measure of the radiant flux against the surface of something (eg radiant flux per unit area).
The SI unit of irradiance is watts per square meter (Watt/m2).
1.4 Radiance
This refers to the radiation intensity per unit projected area of the radiation source.
The SI unit of radiance is watts/square meter steradian (Watt/m2 sr).
2. Spectral radiation measurement
Spectroradiometry is the measurement of light energy at certain wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. It can measure the entire spectrum or a specific bandwidth of wavelengths.
2.1 Spectral radiance
The radiance of a particular light source is a constant value, which is the sum of all energies over the entire spectral range. The energy value for a specific wavelength can be measured by spectral emission brightness.
The SI unit of spectral radiance is watts/m2 steradian nanometers (Watt/m2 sr nm).
2.2 Spectral irradiance
This is a measure of the radiant flux relative to a specific wavelength per unit area.
The SI unit of spectral irradiance is watts per square meter nanometer (Watt/m2 nm).
3. Photometric measurement
Electromagnetic energy can be seen by the human eye in the form of light, so photometry is a measurement of the psychological and physical properties of electromagnetic energy. The use of the word “brightness” to describe light defines that photometry should be based on human perception.
Photometry was an emerging discipline when the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) defined the average sensitivity of the human eye in 1942. CIE determined photoadaptation data for a large number of human samples, which were then compiled into the CIE standard photometric function. The function includes the photopic curve – color perception in normal conditions, and the scotopic curve – achromatic perception in low light conditions. (See below)
The relative sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths.
The photometric values correspond to the radiometric values in the CIE standard luminous efficiency function. We can think of the optical efficiency function as a transfer function of a filter that approximates the performance of the human eye.
Photometry includes four concepts, called luminous flux, light intensity, illuminance, and brightness.
3.1 Luminous flux
Light sources radiate energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. We use flux to describe light energy. Luminous flux is a measure of the flux of light energy emitted by a light source or received by a surface. The luminous flux value (CIE standard luminous efficiency function, Vλ) is obtained from the radiant flux by estimating the radiance of the photometric efficiency corresponding to the standard eye.
The unit is lumens (lm)
lm = 683 x W (Watt) x V λ
3.2 Light Intensity
This describes the intensity of the light source in a certain direction, defined as the amount of luminous flux emitted into a unit solid angle.
Luminous intensity is referred to as light intensity or luminosity in photometry. A physical quantity used to represent the luminous flux per unit solid angle in a given direction of a light source. The international unit is candela, symbol: cd, formerly known as candlelight.
The definition of luminous intensity considers human visual factors and optical characteristics, and is established on the basis of human vision.
Confusingly, in optics, light intensity often refers to the radiant power per unit area. Since the relative visibility of the human eye to different wavelengths of light is different, when the radiant power of different wavelengths of light is equal, the luminous flux is not equal.
The unit is candela (cd)
1 cd = 1 lumen per steradian (In practice, one candela is roughly equal to one candle.)
3.3 Illumination
This is a measure of the luminous flux on a surface, expressed in lumens per unit area.
Illuminance is a physical term that refers to the luminous flux of visible light received per unit area. Unit Lux (Lux or lx). The amount used to indicate the intensity of the light and how well the surface area of the object is illuminated.
In photometry, “luminosity” is the density of luminous intensity in a specified direction, but is often misunderstood as illuminance. The international unit of luminosity is the candlelight received per square meter (called candela in mainland China, Hong Kong and Macau).
Illuminance has a great influence on the photosynthesis of organisms. We can measure illuminance with a light meter.
The unit is lux (Ix)
1 Ix=1 lumen per square meter (Im/m2)
Imperial units are footcandles
1 foot candle = 1 lumen per square foot (Im/ft2)
3.4 Brightness
Brightness is also known as luminosity. Brightness is a setting of the flux emitted or reflected from a projection plane. Academic researchers often call it the light intensity per unit area.
Brightness refers to the ratio of the light intensity of the illuminant to the area of the light source, which is defined as the brightness of the light source unit. That is, the luminous intensity per unit projected area. The unit of brightness is candela per square meter (cd/m2). Unlike illuminance, the objective corresponding quantity defined by physics is light intensity. These two quantities are often confused in common everyday language.
Brightness, also known as lightness, indicates how bright or dark a color is. The brightness perceived by the human eye is determined by the light reflected or transmitted by the color.
The unit is candela per square meter (cd/m2), or nit.
The imperial unit is the foot-lambert (fl).
1 fl = 3.426 cd/m2.


