Introduction to Incandescent Lamps
Incandescent lamps have been used all over the world for more than 100 years since their invention. Incandescent lamps directly add AC mains power to the tungsten filament resistor to make it generate heat and emit light, thereby illuminating the dark. It enables hundreds of millions of people around the world to have the light and happy life brought by electric lights at night, as well as the convenience of work.
Incandescent lamps are electric light sources that heat the filament to an incandescent state and emit visible light by thermal radiation. Since Thomas Edison in the United States made a carbon fiber (ie carbon filament) incandescent lamp in 1879, the luminous efficiency of the incandescent lamp has been improved accordingly through the continuous improvement of the filament material, filament structure and filling gas. However, the luminous efficiency and other optoelectronic parameters of incandescent lamps are worse than those of new light sources such as energy-saving lamps and tungsten halogen lamps, and are gradually being replaced by new light sources.
How to design and manufacture LED lamps to be as convenient as incandescent lamps? This is a major issue facing thousands of LED lighting designers.
Blue light “LED Incandescent” maybe.
Concept of Blue LED Incandescent Light
Traditional white LEDs are directly coated with yellow phosphorous phosphors on blue LEDs. Due to the high heat after the white LED is lit, the yellow phosphorus phosphor is easily denatured under long-term high temperature smoking, resulting in a deterioration of the color rendering index after a long time.
In LED lamps, for example, yellow phosphorous powder is not directly coated on white LEDs, but yellow phosphorous is dyed on PVC lampshades, and a certain distance is maintained from blue LEDs in the lamps. The superimposed use of the two can also obtain the white light or warm white light effect of LED lamps.
Since the yellow phosphorus filter shade is far away from the LED heat source, it will not be aged and degenerated due to long-term high-temperature roasting of the LED light source. CRI (color rendering) is basically unchanged. The formula of the yellow phosphorus filter shade is adjustable, and the color and color temperature of the light can be adjusted according to the needs of customers. It can meet customized requirements and produce differentiated products.
Blue LED incandescent lamps follow the structure design of incandescent lamps to facilitate the inheritance of the use of incandescent lamps for hundreds of years. The connotation of innovation is to give LEDs new technologies that are energy-saving, pollution-free and long-life. Use blue HV LEDs as light source, with yellow phosphor filter shade. The commercial power is converted by AC/DC rectification and constant current drive power supply, and the constant current DC power is output to light up the blue LED light source. The blue light is filtered by the yellow phosphor filter shade for secondary emission, so that the LED incandescent lamp emits cool white light or warm white light.
Key to blue LED technology
In the spring and summer of 2011, when designing the blue LED light engine, designers have already thought of the design of the blue LED incandescent lamp.
Blue light “LED incandescent lamps” have a yellow phosphorous color when not lit due to the use of yellow phosphorous dyed or yellow phosphorous-sprayed PVC shades. When it is powered on, it emits a cool or warm white light. An unlit blue LED incandescent lamp is shown in the image below. Yellow phosphorus dyed or sprayed with yellow phosphorus PVC lampshade is the key technology.
Unlit blue light “LED Incandescent”
LED Light Source Selection
The choice of LED light source for blue LED incandescent lamps is preferably blue HV LEDs. This enables direct lighting with high-voltage direct current. The power supply can be simplified and the cost of the power supply can be reduced, and the space occupied by the power supply can be reduced.
HV LEDs are System-on-Chip (SOC), or modules, that are made directly on silicon wafers during chip production. This is a revolutionary advancement in LED chip manufacturing technology.
On a 2-inch silicon wafer, thousands of LED dies can be produced at one time. However, if it is produced by common technology and process, the discreteness of each LED parameter is very large. Therefore, after production, the manufacturer needs to measure the parameters one by one, and the customer can only use the adjacent three files in one unit (lamp) to ensure the consistency of the displayed light color.
HV LEDs are produced using next-generation processes and sophisticated processing techniques that allow the parameters of thousands of LED dies on the same silicon wafer to be identical. This makes it easy to get close to the HV LEDs that form the SOC during chip production. Such blue HV LEDs are easy to use and controllable in cost.
Another COB blue HV LED is a blue LV LED die with larger discrete parameters produced by the aforementioned general technology. After the test data, configure the same parameters together and reassemble into a light source body. Since LED dies need to be tested, paired, screened, and combined one by one, and there are many scattered parameters that cannot be used in combination, the production cost will be high. The operating current of HV LEDs is 20-60mA. Compared with the 300-700mA current required by low-voltage LEDs, the heat generated during operation is relatively small.
Beam angle
Energy Star requires that the light-emitting angle of the LED bulb must be greater than 270 degrees, so the three-dimensional light-emitting design of the LED light source is the only solution to expand the light-emitting angle of the bulb.
Design a copper through-core pole on the bulb head, and place LED lamp beads or modules around and at the top, so that the light output at the largest angle can be designed to achieve light emission similar to incandescent lamps.
The copper macaroni pole can help the heat dissipation of the LED lamp beads. Due to the limited area of the copper through-core pole, blue LED incandescent lamps can only be applied to 3W low-power bulbs, which are equivalent to 25W incandescent lamps, if they require a larger light-emitting angle.
If the light-emitting area of the bulb close to the lamp head is sacrificed to install an aluminum heat sink, a general-purpose low-voltage blue LED string can be used to design 5W and 7W blue LED incandescent lamps. There are many solutions for the distribution design of the LED light source of the copper through-core pole, and the key technologies will not be described in detail.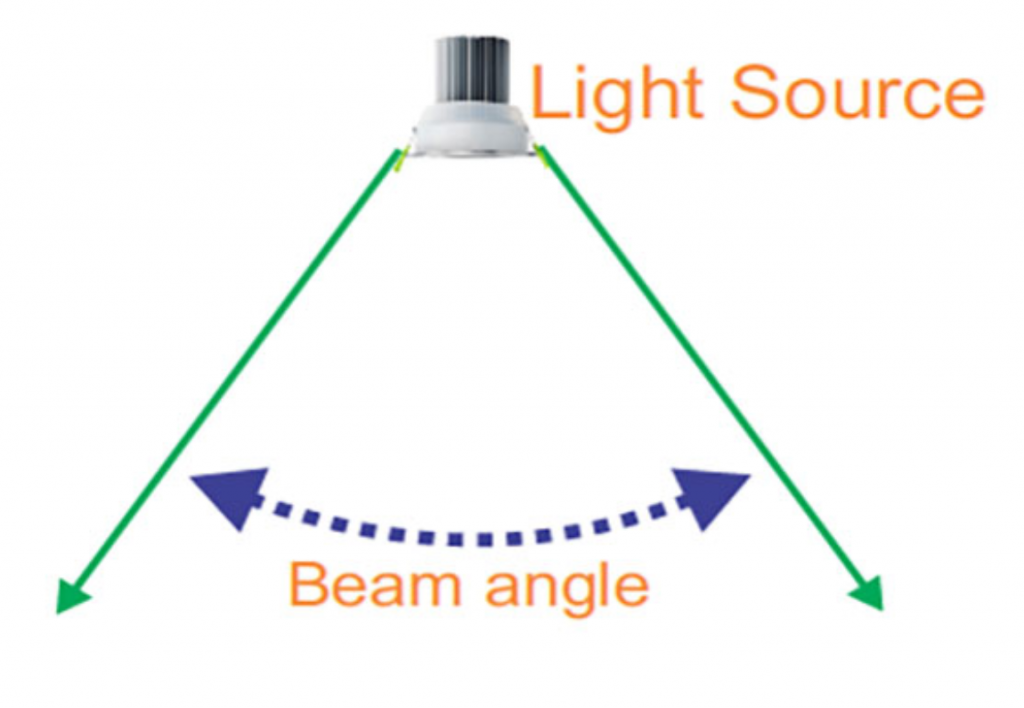
Blue HV LEDs Drive Power Design
There are currently three ways to drive blue HV LEDs:
1) Constant Current Diode (CRD)
A constant current diode (CRD) is a device that can only provide a stable current to the LED light source lamp bead within a certain voltage variation range, which is equivalent to a small constant current source or a limiter for the maximum peak current.
It can ensure a certain current stability when there is a small fluctuation in the power grid. The application circuit is simple, low cost and takes up little space. The performance can only be said to be a little better than that of the resistance-capacitance step-down circuit, which can meet the requirements of LED constant current when the load is small and the grid voltage does not fluctuate much. When the grid voltage fluctuates greatly, it is difficult to stabilize the output current.
The output current of the constant current diode is limited, generally 20-40mA, but it can meet the requirements of high voltage and low current of HV LED. The current required by HV LEDs is typically 20-60mA. The application circuit of the CRD is very simple. When the LED needs a small current such as 20mA and the load is light, a CRD can be selected. When a large current is required, such as 30-60mA, multiple CRDs can be connected in parallel as shown in the figure to expand the current.
2) High voltage linear constant current source driver chip
The linear driver chip may be one of the better solutions for the constant current drive power supply for HV LEDs. EXC100 is one of the more ideal chips. The application circuit is very simple and there are few peripheral parts. The EXC100 uses segmented conduction technology for LED loads. The EXC100 chip has a built-in high-voltage MOS tube. The application circuit has no transformer and no electrolytic capacitor, and there are few peripheral circuit parts. Meet the needs of designing blue light “LED incandescent lamps” in small spaces.
However, the price of EXC100 is too expensive, and the cost of producing popular LED lighting lamps is too high, which is not good for mass sales of products. Only products with good price-performance ratio can prevail in the world.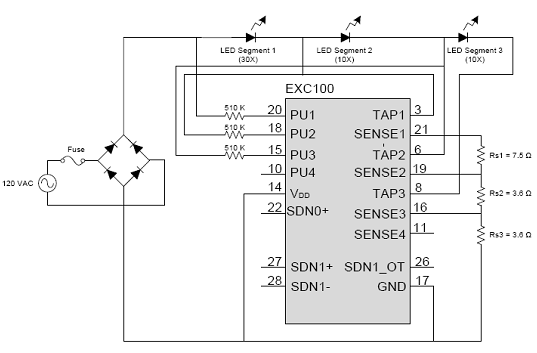
BP5118 is a new linear drive power chip specially designed and produced by a local chip design company for HV LEDs. BP5118 is a high-precision linear constant-current LED control chip, which is mainly used to drive high-voltage, low-current LED light strings or modules powered by mains. Since the application circuit does not require electrolytic capacitors and magnetic components, the LED driver can achieve small size, long life, and EMI compliance.
BP5118 adopts input voltage sampling and LED driving mechanism to change the number of connected LED lights when the input voltage changes. Therefore, in the entire AC cycle, the time that the LED is lit can be increased, thereby improving the utilization rate of the LED and the total output lumens. In order to adapt to different forward voltage drops of LED light strings or different mains voltages (110V, 220V), the switching voltage of light strings can be flexibly set through an external voltage divider resistor.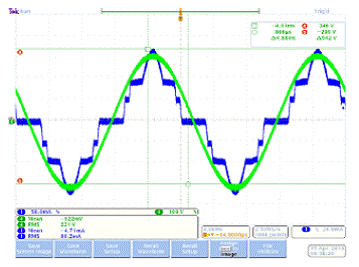
3) High voltage switching constant current source driver chip
There are not many varieties of high-voltage switching constant current source driver chips, BP2812 is one of them. BP2812 is suitable for non-isolated step-down LED power system, suitable for full range of AC input or 12V-600V DC power input. Built-in 600V power MOS tube. Critical mode operation without inductance compensation. The application circuit requires few peripheral components.
The chip has a high-precision current sampling circuit. The patented constant current control technology can achieve high-precision constant current output and excellent load regulation. The system efficiency reaches 95%. Using source drive technology, the chip operating current is as low as 200uA, and no auxiliary winding is required to supply power. With LED short-circuit protection, CS sampling resistor short-circuit protection, chip over-temperature protection and other multiple protection functions. The application circuit is simple and the system cost is low.
Summarize
It can be seen that it is a better choice to use a high-voltage linear constant current source chip to design the driving power supply for the blue LED incandescent lamp.
Blue LED incandescent lamps will become a wonderful flower in LED lighting products, competing for beauty. The blue HV LEDs light source and high-voltage linear constant current source driver chip required for blue LED incandescent lamps have mature products; yellow phosphorus filter lampshade, LED three-dimensional light-emitting lamp post also has room for innovation in production process and design technology. Therefore, many differentiated new products can be derived. The LED lighting market is limitless.