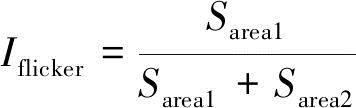1. Evaluation criteria for flickering
At present, the generally accepted flicker evaluation indicators include flicker index, flicker percentage or modulation depth.
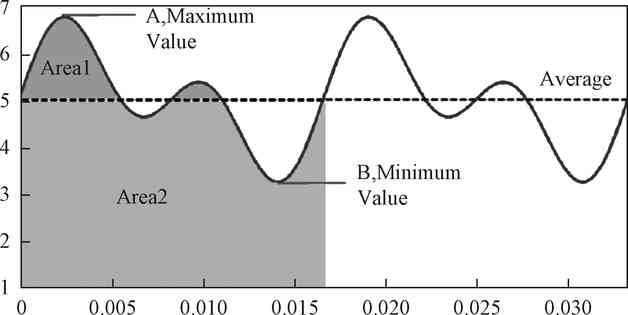
Flicker index (Iflicker) refers to the ratio of the area of the envelope area above the average line of the output light to the area of all envelope areas, as shown in Figure 1 and Equation (1).
Fig.1 Diagram for definition of flicker index and percent flicker
Percent Flicker (Pflicker), namely the modulation percentage (Mod%) or Modulation Depth (Dmodulation), is defined as shown in formula (2).
Fig.1 Diagram for definition of flicker index and percent flicker
Percent Flicker (Pflicker), namely the modulation percentage (Mod%) or Modulation Depth (Dmodulation), is defined as shown in formula (2).
(2)
In the formula, A is the maximum value on the average line of the input light, and B is the maximum value on the average line of the output light.
1) IEC evaluation criteria for flicker
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) evaluation standard for light flicker is part of the electromagnetic compatibility disturbance characteristic evaluation, which is used to evaluate the visual flicker effect of other lighting products due to voltage fluctuations caused by voltage fluctuations during operation of LED lighting products. The frequency range is 0.05 to 80 Hz.
Among them, IEC has done a lot of research on human subjective perception of luminance fluctuations, given sensitivity curves, and designed a set of probability-based flicker analysis methods. In the IEC evaluation standard, the short-term flicker value Pst is used to evaluate the visible light flicker. Typical observation time for Pst is 10 min.
In the calculation, the human subjective perception of light fluctuations is simulated. By analyzing and calculating the instantaneous light flicker visual sensitivity probability, the light flicker severity in this period of time is evaluated. IEC recommends Pst = 1 as the limit, which means that under standard experimental conditions, 50% of the testers can just feel the light flickering phenomenon.
2) US ENERGY STAR content about flickering.
The U.S. Energy Star Lamps V2.1 certification specification came into full effect on October 1, 2017. Compared with version 2.0, Lamps V2.1 has many changes. It adds the measurement and evaluation index of LED light stroboscopic, especially the more detailed requirements for the stroboscopic performance evaluation of dimmable LED lights. A clear requirement is put forward for the light output frequency of the LED light, that is, the frequency f of the LED light output should be greater than 120 Hz.
For all lamps marked as dimmable, the test report provides flicker percentage (Pflicker), flicker index (Iflicker), light output periodic frequency (f), short-term flicker index (Pst), stroboscopic effect visualization parameter (SVM) ), ASSIST flicker perception (Mp) and other parameters measurement results. Among them, Pst, SVM and Mp are newly proposed in Lamps V2.1.
3) CIE research on flicker.
According to the International Commission on Illumination (CIE), the changes in the visual perception of the environment caused by the light output are called Temporal light artefacts (TLAs). In this situation, people will have visual illusions, such as seeing some fast-moving equipment as slow-moving or even stationary. This can cause serious accidents in industrial production. The potential negative effects of the TLA phenomenon have prompted researchers to look for ways to measure it to better understand the extent to which this effect affects the lighting quality of a lighting system.
In order to avoid confusion caused by unclear definitions in the past, CIE defined flicker in 2011 as the unstable performance of visual perception caused by light stimuli whose brightness or spectral distribution fluctuates over time. This suggests that flickering is a perceptual effect, but does not involve the effect of the observer and the surrounding environment.
In 2017, CIE held the International Scintillation Coordination Conference, at which a consensus was reached on the classification of light flickering phenomena, which can be divided into three categories: visual perception, visual efficacy and biological nerves according to their impact on people. According to CIE TN 006-2016 visual perception can be divided into Flicker, Stroboscopic effect and Phantom array effect.
CIE uses the SVM sensitivity index to evaluate the stroboscopic effect, and the frequency range is 80-2000 Hz. And quantify the visibility of transient light effects, that is, “visibility test”, which is represented by “Mv”, as follows: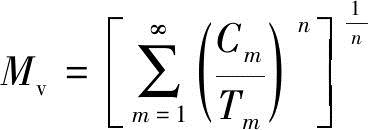
where Cm is the amplitude of the mth Fourier part, Tm is the visibility threshold effect of the sine wave at the frequency of the mth Fourier part, and n is the Minkowski criterion parameter.
(4) The flicker evaluation method recommended by IEEE
The focus in IEEE Std 1789 is flicker as a feature of light source design and construction. The light mentioned in it is all modulated light, or flicker to some extent mainly caused by the AC power supply. And describe the relationship between the frequency and modulation depth and the recommended operating area, as shown in Figure 2. In order to limit the negative physiological effects of flicker on people in general-purpose luminaires, the modulation depth should be guaranteed to be within the shaded area shown in Figure 2. IEEE gives three recommended applications.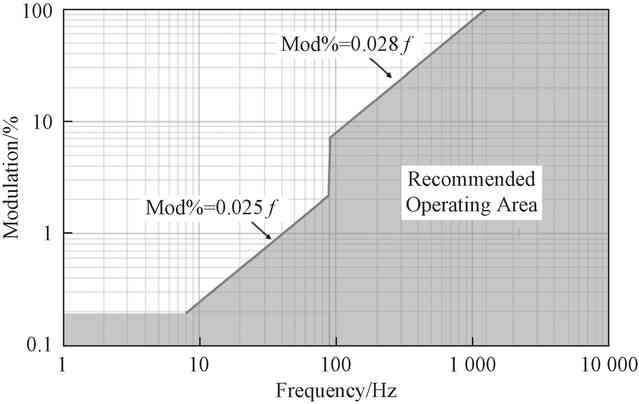
Fig.2 Relationship between Risk Level and frequency and Modulation
Recommended Application 1
– If one wishes to limit the adverse physiological effects of flicker, the flicker modulation percentage should meet the following conditions:
- i) f<90 Hz, modulation percentage (Mod%)<0.025f,
- ii) 90 Hz<f<1 250 Hz, modulation percentage (Mod%)<0.08f,
iii) f>1 250Hz, no requirement for modulation percentage.
Recommended Application 2
– If it is desired to limit flicker to within the invisible level (NOEL), the flicker modulation percentage should be divided by 2.5 to meet the physiological effects of limited flicker in Recommended Application 1:
- i) f < 90 Hz, Modulation percentage (Mod%) < 0.01f,
- ii) 90 Hz < f < 3 000 Hz, Modulation percentage (Mod%) < 0.033 3f,
iii) f > 3 000 Hz, no requirement for percent modulation.
Recommended Application 3 (Precautionary Measures)
– For any light source, under any conditions of use, the flicker modulation percentage shall satisfy:
f < 90 Hz, Modulation percentage (Mod%) < 5%.
(5) Chinese standards for flicker
In GB 17625.2 “Electromagnetic Compatibility Limits on Voltage Variation, Voltage Fluctuation and Flickering in the Public Low-Voltage Power Supply System for Equipment with a Rated Current of ≤16 A per Phase and Unconditional Access”, short-term flicker at the input end of the power supply for lighting products Visible flicker was assessed by the variable index Pst. The typical observation time of Pst is 10 min, which simulates human’s subjective perception of light fluctuations. The severity of light flicker during this period is evaluated by analyzing and calculating the instantaneous flicker visual sensitivity probability. GB/T 31831 “Technical Requirements for LED Indoor Lighting Applications” refers to the fluctuation depth (FPF) limit of light output to evaluate flicker.
2. How to measure flicker
At present, the research on LED lighting flicker is basically based on the fluctuation of light output. The Alliance for Solid State Lighting Systems and Technologies (ASSIST) recommends a method for perceptual evaluation of light flicker, as shown in Figure 3. Using high-resolution, high-sampling frequency ultra-fast photometric probes and fast data analysis systems, it can measure parameters such as flicker frequency, flicker index, flicker percentage, and light fluctuation depth of LED lighting products.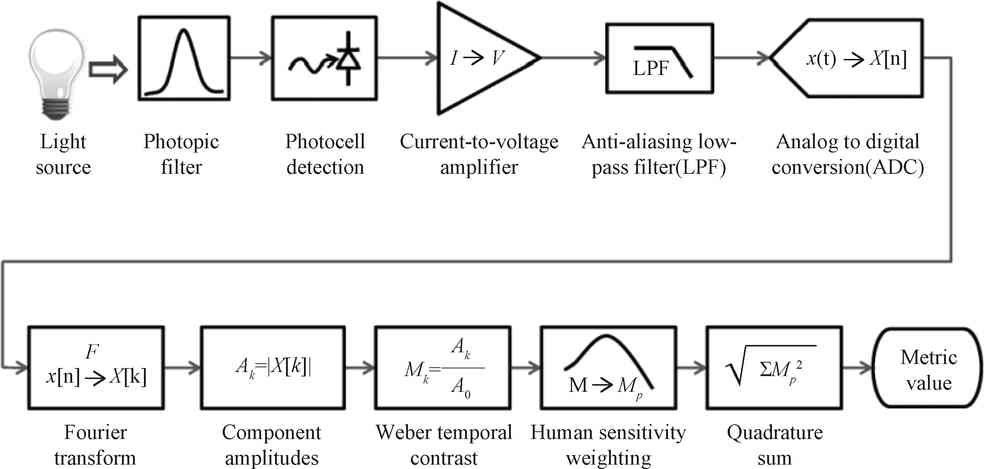
Fig.3 Measure the light waveform and compute the flicker metric
(1) Capture the optical output waveform.
The light output waveform accurately reflects the light output versus time. An oscilloscope is needed here. The general oscilloscope is 8-bit, which can make the sensitivity of the flicker threshold within 0.5%.
The minimum sampling frequency recommended by ASSIST is 2 000 Hz. The minimum sampling frequency required in digital signal analysis theory is at least 2 times the waveform cycle frequency. Most of the light flicker frequency is 2 times the power frequency, about 100 Hz, ie the minimum sampling frequency should be 200 Hz. However, the performance of the actual measurement system is far lower than the theoretical value, so it is recommended that the minimum sampling factor for waveform capture is 10, and the minimum sampling frequency should reach 2 000 Hz.
The minimum sampling recording duration recommended by ASSIST is 2 s. A longer recording time can better reflect the temporal change of light output, especially for waveforms with unstable light output, so the recommended recording time is 10 s.
(2) Fourier transform.
The optical output waveform data goes through analog-to-digital conversion and enters the discrete Fourier transform module. The discrete Fourier transform is defined as follows: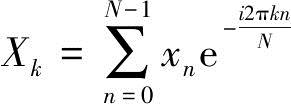
(4)
where Xn is the sampling data, N is the number of sampling times, k represents a frequency integer without a Fourier series, the periodic frequency f=kS/N, S is the sampling frequency, and Xk is the amplitude of the Fourier series.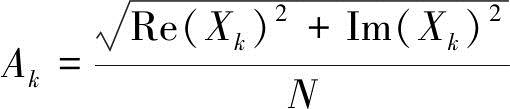
(5)
where Re(Xk) and Im(Xk) are the real and imaginary parts of the Fourier series.
(3) Weber transient constant calculation.
The Weber transient constant is used to represent the modulation ratio by the amplitude of each component of the optical output Fourier, which is represented by M.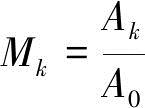
(6)
Among them, Ak is the amplitude of each component of the optical output Fourier. A0 is the DC part of the optical output waveform, that is, the fundamental part. For a single frequency waveform (such as a sine wave), the modulation ratio of the light output is equal to the flicker percentage multiplied by 100%.
(4) Weighted calculation of human perception sensitivity.
The perceptual sensitivity of the human body is defined as the ratio of the Weber transient constant at a single frequency to the human observation threshold at that frequency, as follows: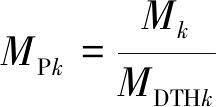
(7)
where MDTHk is the human observation threshold at a single frequency. MPk is 1, which means that 50% of the human body perceives the flicker of this frequency. When MPk is less than 1, flicker cannot be observed. When MPk is greater than 1, flicker is easily observed.
(5) Joint frequency part.
The Combined Frequency Components is the quadratic root value of the square weighted sum of the human perception sensitivity on each frequency component (except the fundamental part).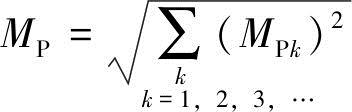
(8)
Mp equals 1, which means that 50% of the human body perceives flickering at this frequency. When the MP value is less than 1, flicker cannot be observed. When MP is greater than 1, flicker is easily observed.
3. Conclusion
IEC only gives the index and measurement method of input current harmonic flicker at the AC power input end of lighting products. This method has been widely used in the EMC certification of LED lighting products.
IEEE gives the relationship between the output light modulation depth and frequency and the flicker hazard level, and gives three recommended thresholds for applications according to different application levels.
On the basis of the light modulation depth, modulation frequency and flicker index and other indicators, ENERGY STAR and CIE introduced new flicker effect visualization parameters and flicker perception parameters according to the visual perception effect of human body on flicker. and strengthen the research on flickering effects in the frequency domain. However, the measurement method of the frequency domain index is complex, affected by the measurement technology, the accuracy and precision of the measurement results are difficult to guarantee, and the measurement cost is also high.
On the one hand, the Chinese national standard adopts the IEC measurement method and standard requirements for the input end of the AC power supply and the harmonic flicker of the input current. On the other hand, it gives detailed requirements for the fluctuation depth and fluctuation frequency of the LED light output for indoor lighting. The minimum limit of the fluctuation depth should be less than 0.288%. It is looser than the limit requirements given by IEEE.