What kind of lamps should be used in common workplaces is also determined by the environment in which they are used. Take factory lighting as an example. If the humidity in the workshop is high, it is necessary to use lamps with good waterproof performance, while in dusty workshops, dust-proof lamps must be used. In these cases, the IP rating of the lamps used must be carefully selected. When choosing lamps and lanterns, also consider the requirements of safety protection. For example, for lamps that can be touched by humans, they should have good protection against electric shock. For flammable and explosive occasions, explosion-proof lamps should be used.
Let’s briefly discuss the characteristics and lighting requirements of factories, ports and gas stations.
Factory lighting requirements
Factory lighting involves a wide range of places and operations, including fine processing in small workshops, heavy industrial production in tall factories, and operations in hazardous situations such as flammable and explosive. Lighting workers must According to different places and the nature of the work, the corresponding design is carried out to provide comfortable and economical lighting for the staff, so as to maximize the productivity, reduce accidents and protect the health of the staff.
Illuminance value
The overall illuminance value (also called the illuminance level) is the most basic requirement in factory lighting. The following table lists the requirements for illuminance in some workplaces in the relevant international standards.
Excerpt from International Illumination Committee Lighting Standard (S008-2001)
Explanation: Em——average illuminance, the average value of illuminance, the larger the value, the brighter the illumination.
| Type of place, job or activity | Em (lx) | Remarks |
| 1. Cement, concrete, and brick factories | ||
| drying | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Prepare materials, mix and load cellar work | 200 | |
| General machine work | 300 | |
| Rough forming | 300 | |
| 2. Chemicals, plastics, rubber factories | ||
| Remote control operation processing device | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Limited manual intervention processing device | 150 | |
| Processing plant area where people often work | 300 | |
| Precision measurement room, laboratory | 500 | |
| Pharmaceutical production | 500 | |
| Tire production | 500 | |
| Color check | 1000 | CCT>6500K |
| Cutting, assembly, inspection | 750 | |
| 3. Electrical industry | ||
| Cable manufacturing | 300 | |
| Entangled | ||
| Large coil | 300 | |
| Medium coil | 500 | |
| Small coil | 750 | |
| Coil injection | 300 | |
| plating | 300 | |
| Assembly work | ||
| -Rough, such as a large transformer | 300 | |
| Medium, such as switchboard | 500 | |
| Details, such as phone | 750 | |
| Fine, such as measuring equipment | 1000 | |
| Electronic workshop, testing room, debugging room | 1500 | |
| 4. food industry | ||
| Brewery workplaces and areas | 200 | |
| Product sorting and washing, grinding | 300 | |
| Slaughterhouse workplaces and areas, milk product mills, filter beds, sugar refining furnaces | 500 | |
| Cutting and sorting of vegetables and fruits | 300 | |
| Cooked food production, kitchen | 500 | |
| Cigar and preparation of tobacco production | 500 | |
| Glassware and bottle inspection, product control, sorting, classification and decoration | 500 | |
| laboratory | 500 | |
| Color check | 1000 | Tcp > 4000K |
| 5. Foundry, metal foundry workshop | ||
| Pedestrian tunnels, cellars, etc. | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| platform | 100 | |
| Prepare sand | 200 | |
| locker room | 200 | |
| Furnace and mixer workplace | 200 | |
| Casting cabin | 200 | |
| Shake out area | 200 | |
| Mechanical casting | 200 | |
| Core casting | 300 | |
| Die casting | 300 | |
| Model building | 500 | |
| 6. Metal work and processing | ||
| Open die forging | 200 | |
| Drip forging, welding, cold forming | 300 | |
| Rough and general processing, tolerance greater than 0.1mm | 300 | |
| Fine processing: grinding, the tolerance is less than 0.1mm | 500 | |
| Scribe and check | 750 | |
| Wire and tube drawing | 300 | |
| Mechanical electroplating>5mm | 200 | |
| Sheet metal production “5mm | 300 | |
| Tool manufacturing, cutting equipment manufacturing | 750 | |
| Assembly | ||
| -Rough | 200 | |
| -general | 300 | |
| -detail | 500 | |
| -fine | 750 | |
| plating | 300 | |
| Tools, templates, fixture production, fine machinery | 1000 | |
| 7. Paper industry | ||
| Pulp grinding | 200 | |
| Paper processing, creping machine, cardboard production | 300 | |
| Standard book binding, such as folding, sorting, gluing, cutting, embossing, stitching | 500 | |
| 8. Power station | ||
| Fuel supply plant | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Boiler Room | 100 | |
| Machine hall | 200 | |
| Auxiliary rooms, such as pump room, condensing room, power distribution room, etc. | 200 | |
| Control room | 500 | 1. The control panel is usually vertical
2. May need dimming |
| 9. metal industry | ||
| Production plant without manual intervention | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Production plants with occasional manual intervention | 150 | |
| Production plant with continuous manual intervention | 200 | |
| Slab storage | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| furnace | 200 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Rolling crane, winding machine, shearing line | 300 | |
| Control platform, control panel | 300 | |
| Test, measure and inspect | 500 | |
| Curved parts of pedestrian underpasses, cellars, etc. | 50 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| 10. Vehicle manufacturing | ||
| Body building and assembly | 500 | |
| Painting, chamber spraying, chamber polishing | 750 | |
| Paint: touch up, check | 1000 | Tcp at least 4000K |
| Car interior decoration production (manual) | 1000 | |
| Finished product inspection | 1000 | |
| 11. Public parking (indoor) | ||
| Access slope (daytime) | 300 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Access ramp (night) | 75 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| Lane | 75 | Safety colors must be identifiable |
| parking lot | 75 | High vertical illuminance improves the ability to prevent people from being unrecognizable, thereby enhancing the sense of security |
| Ticketing | 300 | 1. Avoid reflections from windows
2. Prevent glare from outside |
| 12. airport | ||
| Arrival, departure hall, baggage claim | 200 | High-span lighting |
| Connection area, escalator, conveyor belt | 150 | |
| Customs, passport control | 500 | Vertical illumination is important |
| Waiting hall | 200 | |
| Luggage room | 200 | |
| Security check | 300 | |
| Air traffic control tower | 500 | 1. The lighting must be dimmable
2. Glare from daylight lighting must be avoided |
| Air traffic room | 500 | The lighting must be dimmable |
| Aircraft test and repair warehouse | 500 | High-span lighting |
| Engine test | 500 | High-span lighting |
| Aircraft repair area measurement area | 500 | High-span lighting |
| Passenger platforms and underground passages | 50 | |
| Ticket hall and central hall | 200 | |
| Box office, luggage room, counter | 300 | |
| lounge | 200 | |
Uniformity of illuminance
The ratio of the minimum illuminance to the average illuminance is not less than 0.8.
Simple estimation of average illuminance:
Average illuminance = lumens of all lamps × 85% ÷ total lighting area
The minimum illuminance is generally impossible to calculate, and is usually controlled by mastering the correct pitch-to-height ratio during design.
Light source selection
In factory lighting, what kind of lamps are used is also determined by the environment in which they are used.
If the indoor ambient temperature is too low, such as in frozen food processing plants and cold storage, fluorescent lights should not be used. Not only is it difficult to start fluorescent lamps at low temperatures, but the light output also decreases a lot. At this time, high-intensity discharge lamps can be used for lighting, and incandescent lamps can also be used in some places. In those workplaces with high ambient temperature, such as steel mills and foundries, when using gas discharge lamps, it must be ensured that the working temperature of the ballast does not exceed its maximum allowable temperature. Therefore, suitable gas discharge light sources and lamps must be selected.
If the humidity in the workshop is high, it is necessary to use lamps with good waterproof performance; while in dusty workshops, it is necessary to use dust-proof lamps. In these cases, the IP rating of the lamps used must be carefully selected. When choosing lamps and lanterns, also consider the requirements of safety protection. For example, for lamps that can be touched by humans, they should have good protection against electric shock. For flammable and explosive occasions, explosion-proof lamps should be used.
From the perspective of energy saving, fluorescent lamps and gas discharge lamps are generally more energy-efficient than incandescent lamps under the same illuminance value, and the lowest energy-consumption lamp is LED lamp, which can save at least 70% more energy than other types of lamps.
Emergency lighting (accident lighting) requirements
Accident lighting must be quickly started under normal lighting conditions under normal conditions to complete the function of emergency lighting. The factory must install accident lighting devices and safe evacuation instructions.
Hazardous area lighting requirements
Both the refinery and the oil tank plant have extremely complex plant layouts, with not only major light barriers but also working surfaces of different heights.
Floodlights at high altitudes are installed at several locations outside the hazardous area to provide lighting for safe walking and some piece counting tasks.
In many other places where this system cannot provide sufficient illuminance, it is necessary to install some scattered local lighting fixtures, such as stairs, aisles, valves, and metering areas.
The installation location of these lamps should be carefully selected to avoid glare when viewed from different horizontal directions. Most of the local lighting equipment has bulkheads or well-shaped glass frames, and uses high-pressure or low-pressure gas discharge lamps, and needs to be compatible with the operation and the hazard level of the materials in the area.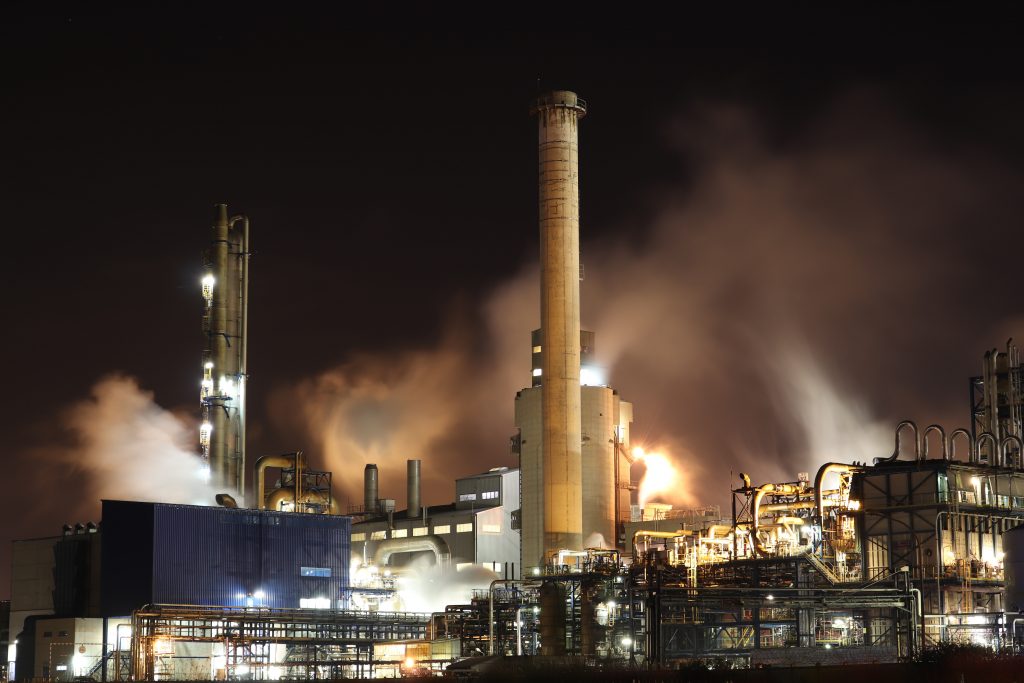
Cargo loading and unloading area and stockyard lighting requirements
These areas are mostly used for the storage and transfer of containers or other large goods, so light barriers have once again become a major design issue. Since most obstacles are movable, fixed local lighting equipment cannot be used.
In addition, the movement of cargo trucks, forklifts, lift arms and gantry cranes must also be considered. Floodlights installed on high poles, high towers or construction sites can provide general lighting for locomotives on rails, vehicles on roads and the safe actions of workers, while local lighting for cargoes is installed on crane racks. The project-light lamp on is completed. Because there will be vibration at these positions, gas discharge lamps with better seismic performance are more suitable, but it must be noted that the fluctuation range of the control voltage cannot exceed the standard of the lamp, otherwise the lamp will be easily damaged.
High-pressure sodium lamps should not be used in places where color recognition is involved. For forklifts, the best choice is ordinary tungsten halogen lamps or low-voltage tungsten halogen lamps. In addition, some local lighting can be added near the fixed hopper machine or conveyor belt.
Port lighting requirements
For the lighting of the wharf, the floodlight should be installed at the periphery of the boundary, so that the light will not be affected by obstacles in the working area, that is, the place of loading and unloading. This arrangement may cast shadows on the decks of ships moored on the shore at low tide. Therefore, there must be floodlighting on the deck and on the crane boom.
The lamps and lanterns on the dock and the deck must be able to withstand the salt-alkali environment of the ocean; the commonly used materials are die-cast aluminum, brass, stainless steel and other plastics. The lamps and lanterns produced by our company have passed the salt spray experiment and can completely resist the marine salt-alkali environment.
In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the lighting on the side of the dock does not interfere with the navigation signal lights. According to the “Port Engineering Technical Specifications” of the Ministry of Communications, the illumination requirements of port lighting are shown in the following table
Illuminance of general lighting in main places in the port
| place | Lowest (lx) | |
| Frontier | Containers | 5 |
| Others | 3 | |
| Yard | Groceries | 3 |
| Containers | 5 | |
| Yard road | 0.5 | |
| Indoor warehouse | 5 | |
| Roads in the port | Main road | 1 |
| Auxiliary road | 0.5 | |
Construction site lighting requirements
There is a special problem on construction sites, because it is mandatory that all equipment that workers on the site may be exposed to must have a voltage equal to or lower than 110V. This means that high-pressure discharge lamps should not be used for lighting except for large civil construction sites that require permanent area lighting systems to be installed during the construction period. Therefore, only special linear fluorescent lamps or incandescent lamps can be used for temporary site lighting. Because the working cycle is usually short and the use conditions of the lamp determine that it only needs to have a short service life, it has to bear a higher electricity bill.
Quarry lighting requirements
The main problem with the lighting of the quarry and open-pit mining is that as the work progresses, the vertical and horizontal extent of the mining area continues to increase. Since the installation of floodlighting may be permanent, the design should be based on the size of the final mining area that can be predicted.
As the distance increases, additional lamps should be installed or lit, and adjustments should be made.
Taking into account the dusty actual situation of such places, adequate maintenance factors and atmospheric loss factors should be considered in the design calculations.
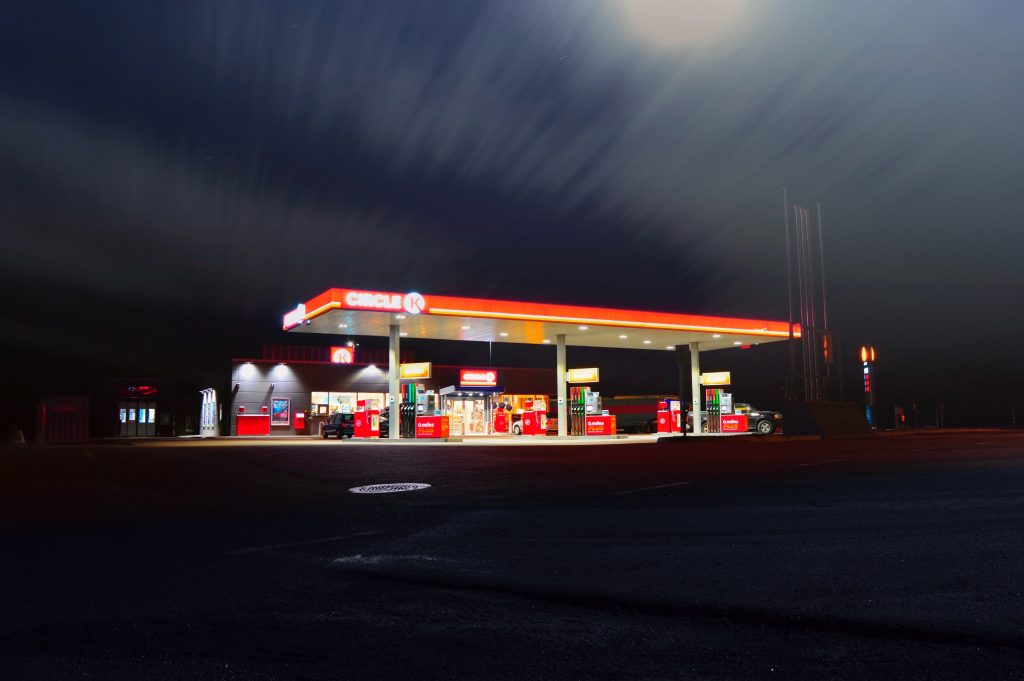
Gas station lighting requirements
The gas station is a highly standardized place. Because of the explosion hazard and toxicity of motor vehicle fuel, it is not easy to control the gas station once an accident occurs. In addition, the number of gas stations is wide, and the number of gas stations has exceeded 100,000 nationwide. The safe operation of gas stations greatly affects the safety of people’s lives and property. Many countries have issued compulsory national standards, and most countries expressly stipulate that the construction of gas stations should strictly implement the “Building Design Fire Protection Code”, and the safety supervision of the construction of gas stations must strictly implement the “Construction Engineering Quality Management Regulations.” , “Implementation of Project Construction and Health Implementation Standards Supervision Regulations” and other laws and regulations.
The task of gas station lighting design is first to establish a sense of security and trust for customers to attract customers to patronize, and secondly, a pleasant consumption experience will ensure that customers come again. Good customer service starts from the moment a customer drives into a gas station, and comfort is the first element to please customers. The International Lighting Association stipulates that the illuminance is greater than 100 lx, but we recommend a design greater than 300 lx.









