The Difference Between Different Spectra
On the spectrogram, we can see that the spectrum of the incandescent lamp is more to the right, and the continuity is stronger. Regardless of whether the LED spectrum is cold white or warm white, it is much more continuous than the fluorescent light spectrum, and the frequency band is also wider.
On the other hand, LED light sources are more biased towards the blue area, while incandescent lamps are more biased towards the red area. This is also in line with the common sense that incandescent lights are yellowish and LED lights are blueish.
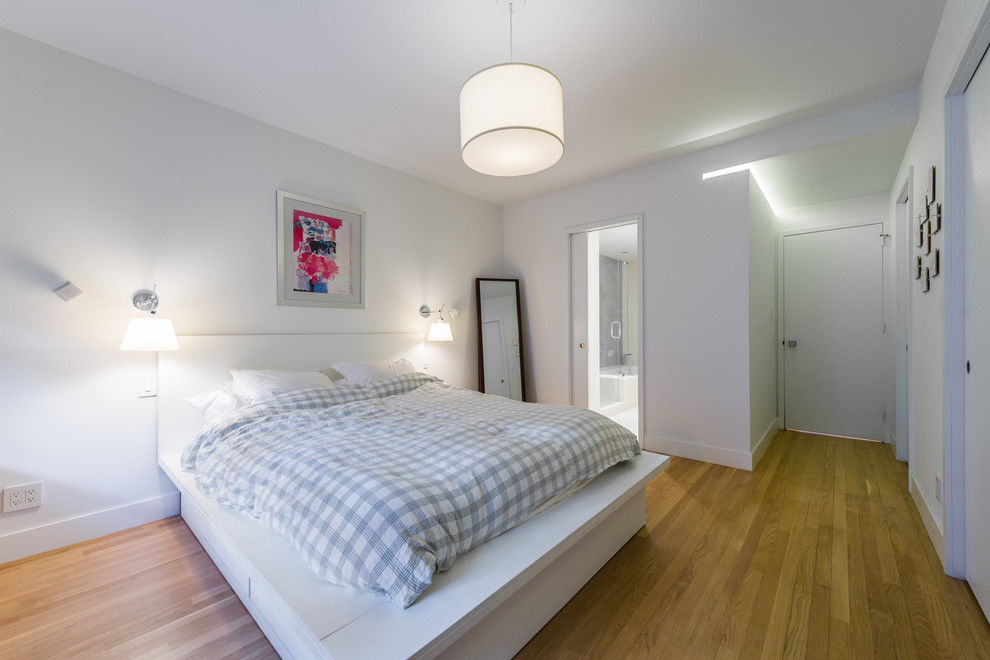
Where it is necessary to truly reflect the original attributes or surface texture of an item or material, a higher color rendering index is required. For example, the changing position of the hallway, the storage and changing position of the wardrobe, the position of the wall painting, the position of the fruit plate of the coffee table, and the position of the dishes on the dining table.
Layered design of lighting
After talking about a few basic concepts, there are still a few issues worth discussing.
Such as the layered design of lighting. This concept includes the difference between full area lighting and local lighting, the difference between functional lighting and atmosphere building lighting, and the difference between fixed lighting and temporary lighting.
For example, use light sources with medium and low color temperatures, medium and low illuminance, and medium and high color rendering properties for auxiliary lighting of decorative items and small spaces. Use about 3800K-5300k color temperature, low to medium color rendering (Ra can be less than 80, of course, you can also use high Ra light source if you have conditions), and a light source with a single point of illuminance greater than 300lx for main lighting to form a lighting level.
Higher color rendering, smaller illumination range, and slightly lower lighting intensity are more suitable for presenting decorative items with lighter colors, and it is not easy to snatch the visual center of a certain wall.
In addition to layered lighting, there are several items mentioned above, namely the echo and coordination of indoor materials and light source lamps, the influence of lighting appliances on the overall layout of the interior design and the setting of the visual center of gravity, reducing glare and avoiding indoor light pollution.
reflection of light
In the use of indoor light, reflection and feedback must also be considered.
This should include both specular reflection and diffuse reflection. Light-colored all-ceramic floor tiles, glass partition doors, glass countertops and other bright surfaces can be approximated as specular reflection materials. The latex painted wall (including the top surface), wallpaper wall, sofa leather surface, sofa art surface and most other indoor material surfaces can be approximated as diffuse reflection surfaces.
Reasonable use of diffuse reflection surfaces and indirect lighting can reduce the effects of glare and avoid indoor light pollution as much as possible.
There are also some other indoor materials (mainly including floors, tiles, stone, indoor doors, door covers, skirting, balcony partitions, etc.) with different reflective properties. In the lighting design, the color rendering of the light source, the color temperature, and the reflection characteristics of the material surface should also be coordinated according to the material characteristics of the above-mentioned items.
For example, indoor doors and door covers, the surface material of the white sticker and the surface material of the white paint have different visual effects under the same color temperature and color rendering. There are similar differences between the white and light yellow wood grain color, the light yellow wood grain color and walnut color, and the yellow log color and dark red lacquer.
Direction of light
In the same way, the angle and direction of light emission from lamps and lanterns and the location of household appliances (mainly refrigerators, which may block direct light) and main furniture also need to be predicted and coordinated. And predict in advance the color temperature and illuminance of the light source and the projection effect on the surface of the furniture to be purchased.
The style and surface material of some electrical appliances also need to be taken into consideration. For example, the refrigerator may be placed in the dining area, and the cabinet door may have white glossy surface, gray metal brushed surface, champagne glossy surface and other different textures. Even under the same light source, different effects will appear.
Reference program for interior lighting design
1. Clarify the purpose and purpose of lighting facilities.
Clarify the nature of the environment, such as offices, shopping malls, and sports venues. Determine the purpose of lighting, determine the purpose that needs to be achieved by lighting facilities, such as function or atmosphere.
2. Determine the appropriate illuminance.
Determine the appropriate illuminance according to the purpose of lighting or use requirements, and determine the illuminance distribution according to the use requirements. According to the nature of the activity, the activity environment and visual conditions, the illuminance standard is selected.
3. Lighting quality.
Consider the brightness distribution in the field of view, the brightest brightness in the room, and the ratio of the brightness of the working surface to the brightness of the darkest surface. At the same time, the brightness and chromaticity ratio between the subject and the background should be considered.
The directivity and diffusivity of light. Generally, there is a need to have obvious shadows and light on a glossy surface. Choose an indicative light source. In order to obtain shadow-free lighting, you should choose a diffusive light source.
Avoid glare. The brightness of the light source should not be too high, increase the angle between the line of sight and the light source, increase the brightness around the light source, and avoid reflected glare.
4. Select the light source.
Consider the color light effect and its psychological effects. Fluorescent lamps can be used in workplaces where color recognition is required and rooms with insufficient natural light. The discoloration and deformation of the target object, the equivalent color effect and atmosphere of interior decoration, etc.
Compared with the luminous efficiency, the luminous efficiency of the general high-power light source is high, and the general fluorescent lamp is 3-4 times that of the white woven lamp. Considering the use time of the light source, the white fabric lamp is about 1000 hours, and the fluorescent lamp is about 3000 hours. Considering the influence of the surface temperature of the bulb, the surface temperature of the white woven lamp is different in various placement directions, and the surface temperature of the fluorescent lamp is about 40.
5. Determine the lighting method.
Choose the type of lighting according to specific requirements. Classification according to the type of lighting on the movable surface: direct lighting, semi-direct lighting, diffuse lighting (completely diffuse lighting and indirect lighting), semi-indirect lighting, indirect lighting, ceiling lamp and trowel lighting, chandelier semi-indirect lighting and wall lamp semi-indirect lighting . Table lamps and projection lamps belong to direct lighting.
Classification according to the illuminance distribution on the movable surface: general lighting, partial lighting, mixed lighting, luminous ceiling design, light eaves (or light trough), light beam (or light strip), luminous ceiling, etc. (with grid or diffuser material)
6. The choice of illuminator.
The main points of selection are the efficiency of the lamp, the light distribution and brightness, the form and color of the lamp. Consider the harmony with the overall interior design. With exposed lamps, the glare becomes larger as the depth of the room increases. This is also the case with lamps with an open bottom, but with less glare than semi-cut lamps. Mirror-type cut-off lamps (without shielding) and prism panel-type lamps have the effect of limiting glare.
Determination of the location of the luminaire. Illumination calculation, point-by-point calculation method: direct illumination of various light sources (points, lines, belts, surfaces). Calculation of uniform illuminance, using coefficient method: at the same time determine the number, capacity and layout of lamps.