What Is Light Intensity
The luminous intensity of a luminous body in a given direction is the luminous flux dΦ transmitted by the luminous body in the solid angle element dΩ of the direction, that is, the luminous flux per unit solid angle. The unit is candela (cd), 1cd=1lm/sr.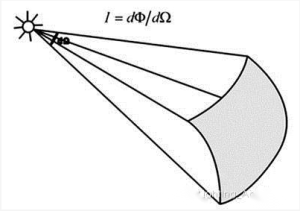
The solid angle can be described by the taper angle of a cone. Light intensity is the value of the luminous flux contained in an infinitesimal cone divided by the solid angle of the cone. It is very useful when calculating the illuminance of a certain point or a small area of accent lighting, and it is also a quantity for judging the illumination distance of lighting equipment.
For example, to calculate the horizontal illuminance (Ehor) of point P: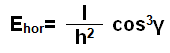
where I is the light intensity.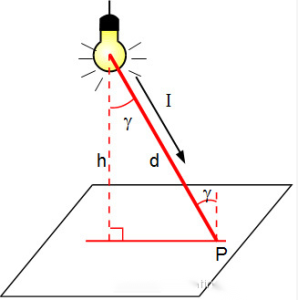
What Is the Relationship Between Luminous Flux and Light Intensity?
A cosine radiator, also known as a Lambert radiator, refers to a luminous body (whether self-luminous or reflected light) whose spatial distribution of luminous intensity conforms to the cosine law. Its radiation intensity at different angles will change according to the cosine formula, the larger the angle, the weaker the intensity.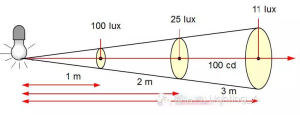
If the light is uniformly distributed in all directions, the light intensity I of the light source in any direction is equal to the luminous flux divided by 4π. For example, a 1000 lumens incandescent lamp housed in an opalescent glass bulb with a transmittance of 0.9 has an intensity of 1000 x 0.9 / 4π = 72 cd in all directions.
What Is the Relationship Between Illuminance and Light Intensity?
The illuminance of a point on a plane perpendicular to the direction of light incidence is equal to the light intensity in the direction of the point divided by the square of the distance between the (point) light source and the point (when the distance is greater than five times the maximum size of the light source, the light source as a point light source), the so-called inverse square law. The calculation formula is: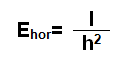
What Are the Main Applications of Light Intensity?
Although the light intensity represents the strength of each beam of light emitted by the lamp. However, the current simulation calculation of lighting is replaced by computer, so the main application of light intensity is to preliminarily judge the illumination distance of lamps, so as to select suitable lamps.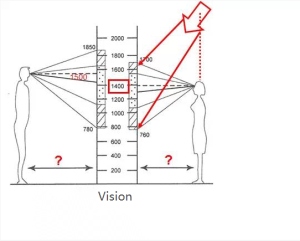
As in commercial lighting, the position of the luminaire can be determined by the position of the observer and the position of the illuminated object. How far the exposure is determined by the light intensity of the lamp. Of course, the size of the beam angle and the influence of the reflected brightness of the illuminated object on the observer should also be considered. By calculating the adjustment angle of the lamp, combined with the key lighting coefficient, we can calculate the visual beam angle (VBA) of the lamp, so as to obtain the luminous flux and beam angle of the lamp, and then inversely calculate the actual power of the lamp. In addition, the color temperature and color rendering of the lamps can also be obtained according to the color of the illuminated object, so that we know what lamps to use.




