The principle of LED color temperature adjustment brightness
Led color temperature is to change the ratio of different lights. Increasing red light makes the color temperature warmer, and increasing blue light makes the color temperature cooler. Adjust the brightness, change the current flowing through the LED, the larger the current, the brighter. Otherwise, it will be darker. The current adjustment is realized by changing the PWM. The so-called PWM is pulse width adjustment. The most fundamental method of pulse width adjustment is to change the value of the resistance and capacitance that determine its width. If the product of RC is larger, the width will be larger.
Dimming and color-adjusting LED lights actually have 2 internal outputs. One way is warm light (about 3000k color temperature), and the other way is cold light (right white, about 6500k color temperature). Each way is independent. By giving each channel a different brightness, the color temperature and brightness of the entire lamp can be adjusted. For example, channel A is warm light and the color temperature is 3000k, but the brightness is only 10% of full brightness, while channel B is cold light, and the brightness is only 40% of full brightness. Then, the color temperature mixed in the lamp body may be only 5000k (not very Cool white, but also a little warm white). In other words, the real dimming and color adjustment can be adjusted from brightness and color temperature.
A new method to realize the color temperature adjustment of LED lamps
The conventional color temperature adjustment method uses two dimming power supplies to drive a white LED array with two color temperatures, high and low, and adjusts the color temperature by adjusting the ratio of the driving current of the two LEDs. This method can only achieve color temperature adjustment, but cannot achieve linear dimming. For this reason, based on the analysis of the problems existing in the conventional method of LED color temperature adjustment, this article proposes a new method of LED color temperature adjustment, and discusses with you that the new method uses only one LED dimming power supply. Only adding a few devices can realize the color temperature adjustment and brightness adjustment of the LED lamps without interfering with each other, which is beneficial to reduce the cost, improve the reliability of the power supply, and has application value for the control of the LED.
1. The conventional method of LED color temperature adjustment
1). The conventional method of LED color temperature adjustment
LED color temperature adjustable lamps use white LED arrays with high and low color temperatures. The two LED arrays are arranged densely and alternately to make the two color temperatures fully mixed. The overall color temperature can be adjusted by adjusting the ratio of the driving current of the two LEDs. The PWM1 signal is used to adjust the output current I1 of the dimmable power supply P1, I1 drives the warm white LED array; the PWM2 signal is used to adjust the output current I2 of the dimmable power supply P2, and I2 drives the cool white LED array. By adjusting the duty ratio of the PWM1 signal and the PWM2 signal, the brightness ratio of the warm white LED array and the cool white LED array is adjusted. Due to the sufficient mixing of the two LEDs, the overall temperature adjustment of the lamp is realized.
2). Problems with conventional methods of LED color temperature adjustment
People often don’t want the brightness of the light to change when the color temperature is adjusted or the color temperature to be significantly shifted when dimming, that is to say, it is hoped that the color temperature and dimming will not interfere with each other. Much light environment. However, the above scheme is difficult to meet this requirement.
A. Difficult to achieve brightness adjustment
In most mature LED dimmable driving power solutions, the power management chip usually only provides one dimming pin. When using the above conventional method to adjust the color temperature, in order to achieve the adjustment of the output current ratio of the dual power supply, the dimming pins of the two power supplies will be occupied, so there is no hardware resource for achieving independent dimming while adjusting the color temperature.
B. The power supply efficiency is too low, which reduces the power supply reliability
Because LED is a low-voltage DC light source, the LED driving power supply is a step-down AC-DC constant current power supply. The efficiency of this power supply decreases as the power of the power supply decreases. Using Fujitsu MB39C602 chip LED power supply efficiency with input power measured data, the power supply efficiency when the input power is 3W compared to the input power of 15.5W, the efficiency is reduced by 17%. In the conventional method of color temperature adjustment, there may always be a power supply with a small input power. This means that the efficiency of the power supply decreases and the power loss increases. The power loss is mainly manifested as heat energy in the power supply and generates a temperature rise higher than the ambient temperature. Experience has shown that for every 10°C increase in temperature, the probability of system failure doubles, which will greatly reduce the reliability of the system. On the other hand, the increase in power consumption will lead to a decrease in light efficiency, weakening the energy-saving advantages of LEDs.
2. New method of LED color temperature adjustment
1) A new method of LED color temperature adjustment
The new method adopts the PWM dimming drive power scheme, and adds a color temperature adjustment circuit to the back-end circuit of the power supply. The color temperature adjustment circuit uses PWM switch dimming to adjust the ratio of the on-time of the cool white LED array and the warm white LED array , Realize color temperature adjustment.
This solution uses the PWM1 signal to control the dimming terminal of the power supply, and adjusts the output current Io of the LED by adjusting the duty cycle of PWM1 to realize the dimming of the LED lamp. In order to achieve color temperature adjustment, a cold white LED array and a warm white LED array with a relatively close conduction voltage drop are connected to the output terminal of the power supply, and power switches MOS1 and MOS2 are used to control the on-off and warm white of the cold white LED array respectively The on and off of the LED array. The PWM2 signal is connected to the gate of MOS1 to control the conduction time of the cold white LED array. PWM2 gets an inverted signal after the inverter. PWM3 is connected to the gate of MOS2 to control the conduction time of the warm white LED array. When PWM2 is high, PWM3 is low, so the cold white LED array is turned on and the warm white LED array is turned off, and vice versa. Adjusting the duty cycle of PWM2 to adjust the ratio of the on-time of the cool white LED array and the warm white LED array per unit time, the use of the presence of the human eye to achieve the effect of changing the color temperature.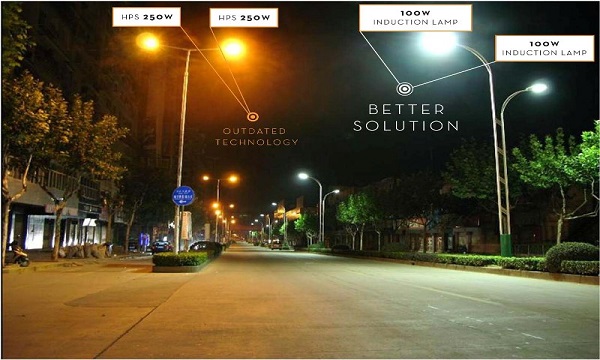
2) Test verification of the new method
In order to verify this method, this article adopts the LED dimming scheme of MB39C602, adds the above-mentioned color temperature adjustment circuit at its back end, and conducts a test. When the color temperature is not adjusted, but only the brightness is adjusted, the color temperature changes with the power. The five typical application color temperature gradient curves of cool white, cool white, neutral white, warm white, and warm white all tend to a parallel line, indicating that only the brightness is adjusted when the color temperature is not adjusted, and the color temperature does not change much. When the brightness is not adjusted and only the color temperature is adjusted, the power changes with the change of the color temperature. There are three power gradients commonly used in practice, and the three power gradient curves all tend to a parallel line, indicating that only adjusting the color temperature when the brightness is not adjusted has little effect on the input power.
It can be seen from the above test results that the new method can satisfy a wide range of color temperature adjustment of LED lamps under different brightness conditions. When only adjusting the color temperature without adjusting the brightness, the input power of the power supply fluctuates little and the luminous flux does not change much. When the color temperature is not adjusted and only the brightness is adjusted, the color temperature changes little. It can meet the requirements of independent adjustment of color temperature and independent dimming. This solves the problem that the conventional method of LED color temperature adjustment can only adjust the color temperature and is difficult to achieve dimming, and at the same time avoids the problem of reducing power efficiency and LED light efficiency due to low power output power.
3) Advantages of the new method
A. The new method can adjust the light and color temperature without disturbing each other
The new method uses independent PWM1 signal and PWM2 signal to control the dimming terminal of the power supply and the control terminal of the color temperature adjustment circuit respectively, so that brightness adjustment and color temperature adjustment do not interfere with each other, and more light environments can be configured to meet more lighting needs.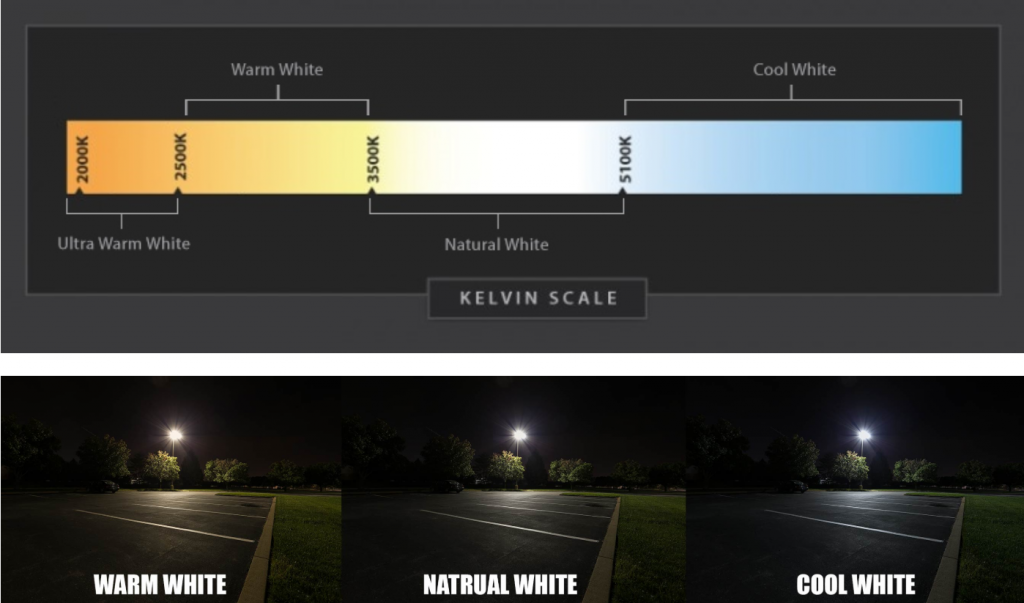
B. The new method is highly reliable
In the new method, at any time, only one of the two high and low color temperature white LED arrays is in the on state, achieving a constant output power, thus avoiding the low power supply efficiency, low system reliability, and light power caused by the low power supply in the conventional method. Problems such as low efficiency.
C. The new method is low cost
The new method has a simple circuit structure, using only one dimming power supply and several devices for color temperature adjustment. Compared with the conventional method using two dimming power supplies, it has the characteristics of low hardware cost, easy control and stable operation.



