Luminaires refer to appliances that can transmit light, distribute and change the light distribution of the light source, including all the parts and components needed to fix and protect the light source except the light source, as well as the wiring accessories necessary for connection with the power source.
General Classification of Lamps
- Lighting
Indoor lighting / outdoor lighting
Indoor lighting—commercial lighting, office lighting and home lighting.
Outdoor lamps—spot lamps, street lamps, high ceiling lamps, tunnel lamps, courtyard lamps, lawn lamps, underground lamps, fireplaces, underwater lamps, etc.
- Commercial lighting
Grill lights, spotlights, downlights, ceiling lights, wall lights, electrical boxes.
- Office lighting
Grill light panels, brackets, emergency lighting.
- Home lighting
European style lamps, ceiling lamps, crystal lamps, decorative lamps, table lamps, floor lamps, sheepskin lamps, cloth shade lamps, mirror lamps, work lamps, kitchen and bathroom lamps, low-voltage lamps, room lamps, candle lamps, yellow sand glass lamps, chandelier wall lamps, etc. .
- Decorative lights
Neon lights, lanterns, lanterns, revolving lanterns, cartoon lights, palace lanterns, etc…
- Warning light
Navigation lights, traffic lights, police lights, etc…
- Special function lights
Shadowless lights, searchlights, follow lights, etc…
- LED lights
(1) Definition
Lamps using LED as light source. Because the LED itself has high brightness, energy saving and environmental protection, all LED lights have the energy saving characteristics of LED.
(2) Optical characteristics
The LED provides monochromatic light with a large half-width. Since the energy gap of the semiconductor decreases with the increase in temperature, the peak wavelength emitted by it increases with the increase in temperature, that is, the spectrum is red shifted, and the temperature coefficient is +2 ~3A/.
The LED luminous brightness L is approximately proportional to the forward current: K is the proportional coefficient.
As the current increases, the luminous brightness also increases approximately. In addition, the luminous brightness is also related to the ambient temperature. When the ambient temperature is high, the recombination efficiency decreases and the luminous intensity decreases.
(3) Thermal characteristics
Under small current, the LED temperature rise is not obvious. If the ambient temperature is high, the dominant wavelength of the LED will be red-shifted, the brightness will decrease, and the uniformity and consistency of the luminescence will deteriorate.
In particular, the temperature rise of dot matrix and large display screens has a more significant impact on the reliability and stability of LEDs.
Lighting Style Classification
- Modern Style
Simplicity, alternative, and the pursuit of fashion are the biggest characteristics of modern lamps.
The material is generally made of metallic aluminum, alternative glass, etc. The appearance and shape are mainly alternative expression techniques, and the colors are mostly white and metallic, which are more suitable for matching with simple and modern decoration styles.
- European style
Similar to the European-style decoration style that emphasizes gorgeous decoration, strong colors, and exquisite shapes to achieve graceful and luxurious decoration effects, European-style lamps focus on curvilinear shapes and magnificent colors. Some lamps will deliberately create a mottled effect with rust, black paint, etc., in pursuit of a sense of imitation.
From the material point of view, European-style lamps are mostly made of resin and iron. Among them, the resin lamp has many shapes, which can have a variety of patterns, and the gold foil and silver foil are affixed to appear bright in color and bright in color; the shape of iron art is relatively simple, but it is more textured.
- American Style
Compared with European-style lamps, American-style lamps seem to be the same. The materials used are the same. American-style lamps still pay attention to classic feelings, but are relatively simple in style and shape, simple and generous in appearance, and pay more attention to leisure and comfort.
The materials used are the same as European lamps, mostly resin and iron.
- Chinese style
Compared with the traditional Chinese style, which is symmetrical and meticulously crafted, the Chinese lamp also pays attention to the contrast of colors. The patterns are mostly Chinese elements such as Shanghe in the Qingming Festival, such as intention, dragon and phoenix, and Beijing opera facial makeup, emphasizing the feeling of classical and traditional cultural charm.
The decoration of Chinese-style lamps is mostly hollow or carved wood, which is quiet and simple. The imitated sheepskin lighting is soft and warm, and it is installed at home, giving people a warm and peaceful feeling.
The sheepskin lamps are mainly round and square.
The round lights are mostly decorative lights, which play a finishing touch in the home;
The square-shaped imitation sheepskin lamps are mostly ceiling lamps, with various fences and graphics on the periphery, which are simple and dignified, simple and generous.
At present, Chinese-style lamps are also divided into pure Chinese style and simple Chinese style. The pure Chinese style is more classical, while the simple Chinese style just uses a little Chinese element in the decoration.
Lighting function classification
- Direct lighting type
The light is emitted through the lamp, and 90%-100% of the luminous flux reaches the assumed working surface
This lighting method has a strong contrast between light and dark, and can create interesting and vivid light and shadow effects, which can highlight the dominant position of the work surface in the entire environment, but due to the high brightness, the generation of glare should be prevented. Such as factories, general offices, etc.
- [Semi-direct lighting type]
The lampshade made of translucent material covers the upper part of the light source, and more than 60%-90% of the light is concentrated on the working surface, and 10%-40% of the covered light is diffused by the translucent lampshade and diffused upward. The light is relatively soft.
Such lamps are often used for general lighting in lower rooms. Because the diffused light can illuminate the flat roof, the height of the top of the room is increased, which can produce a higher sense of space.
- Indirect lighting type
It is a lighting method of indirect light generated by shielding the light source. Among them, 90%-100% of the luminous flux acts on the working surface through the ceiling or wall reflection, and the light below 10% directly illuminates the working surface. Places such as shopping malls, clothing stores, meeting rooms, etc., are generally used as ambient lighting or to increase the brightness of the scene.
- Semi-indirect lighting type
Contrary to semi-direct lighting, the translucent lampshade is installed under the light source, and more than 60% of the light is directed to the flat top to form an indirect light source, and 10%-40% of the light is diffused downwards through the lampshade.
This way can produce a special lighting effect, so that the lower room has a sense of heightened. It is also suitable for small spaces in residences, such as halls, aisles, clothing stores, etc. Usually it is most appropriate to use this kind of lighting in a learning environment.
- Diffuse lighting type
Use the refraction function of the lamp to control the glare and diffuse the light around. There are basically two forms of this kind of lighting. One is that light is emitted from the upper mouth of the lampshade and reflected by the flat top. The two sides are diffused from the translucent lampshade, and the lower part is diffused from the grille.
The other is to use a translucent lampshade to enclose and diffuse the light. This kind of lighting has soft light performance and comfortable vision, which is suitable for bedrooms.
Terms of commonly used parameters of lighting
- Green lighting
Through scientific lighting design, the use of high-efficiency, long-life, safe and stable performance luminaire products will ultimately achieve a lighting system that is efficient, comfortable, safe, economical, beneficial to the environment, improves people’s physical and mental health, and reflects modern civilization.
- Energy Saving Lamp
Refers to lighting products that consume less power and achieve higher lighting effects, such as fluorescent lamps, ring lamps, straight tube fluorescent lamps, compact fluorescent lamps, etc.
- Optical Wit Rate
The lamp is ignited under specified conditions, and the ratio of the luminous flux of the lamp during a specific time during the life of the lamp to the initial luminous flux of the lamp, expressed as a percentage.
National standard requirements: 2000h not less than 78%.
International advanced level: 2000h not less than 90%.
Chinese level: Companies that focus on quality and adopt protective film technology can basically meet international standards.
- Power factor
The product of the effective value of the voltage and the effective value of the current in an AC circuit is the apparent power, and the active power is only a part of it.
The power factor is the ratio of the active power of the lamp to the apparent power.
The lower the power factor, the higher the harmonic content in the current, which will pollute the power grid, destroy the balance of the power grid, and increase reactive power losses.
- Color rendering index
A parameter that measures the ability of a light source to display the true color of an illuminated object. A light source with a high color rendering index (0-100) can reproduce colors closer to natural primary colors. Low color rendering index causes color distortion. The following is the color rendering index of commonly used lamps: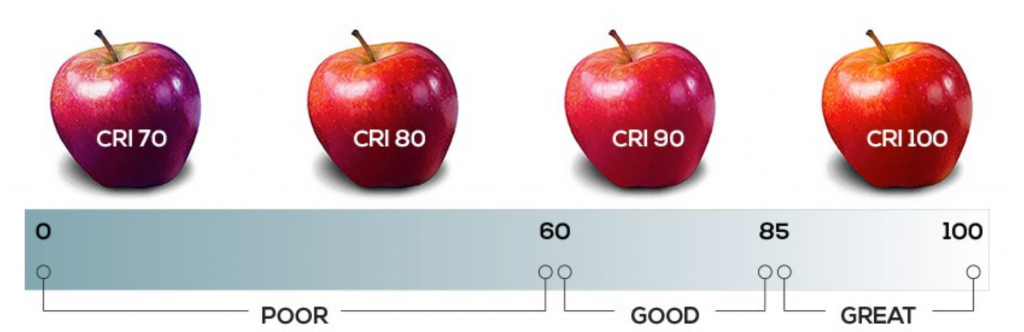
Incandescent lamp—95
Tube type fluorescent lamp—65-80
Tri-color rare earth fluorescent lamp — around 80
High pressure sodium lamp—25-60
Metal halide lamp—70-90
- Color temperature
When the color of the light emitted by the light source is the same as the color radiated by the “black body” at a certain temperature, the temperature of the “black body” is called the color temperature of the light source.
The higher the temperature of the “black body”, the more blue components in the spectrum, and the less red components.
For example: the light color of an incandescent lamp is warm white, and its color temperature is about 2700K, while the color temperature of a daylight fluorescent lamp is about 6400K. Unit: Kelvin (K).
The color temperature of incandescent lamps is generally about 2700K, the color temperature of fluorescent lamps is about 2700-6400K, and the color temperature of sodium lamps is about 2000K. </p>
- Light effect
The efficiency of the light source in converting electrical energy into visible light, that is, the light emitted by the light source consuming every watt of electrical energy. The higher the value, the higher the efficiency of the light source.
From the perspective of economy (energy efficiency), light efficiency is an important parameter. Unit: Lumen/Watt (lm/w).
Incandescent lamp: 8-14lm/W
Single-ended fluorescent lamp: 55-80 lm/W
High pressure sodium lamp: 80-140 lm/W
Self-ballasted fluorescent lamp: 50-70 lm/W
Metal halide lamp: 60-90 lm/W
Tungsten halogen lamp: 15-20 lm/W
- Illumination
The luminous flux received on the illuminated surface of the unit is called illuminance. If the luminous flux received on the illuminated surface per square meter is 1 (lm), the illuminance is 1 (lx).
Unit: Lux (lx). 1 Lux (lx) is equivalent to the illuminance when the luminous flux per square meter is 1 lumen (lm).
The ground illuminance at noon with strong sunlight in summer is about 5000 lx, the ground illuminance on a sunny day in winter is about 2000 lx, and the ground illuminance on a clear moon night is about 0.2 lx.
- Luminous Flux
The sum of the energy emitted by the light source and received by human eyes is the luminous flux. Unit: Lumen (lm), symbol Φ,.
In general, the higher the power of the same type of lamp, the greater the luminous flux.
- Average life span
It refers to the cumulative time when the lamp’s luminous flux maintenance rate meets the requirements of the national standard and can continue to ignite until 50% of the lamp reaches the life of a single lamp (that is, the life when 50% of the lamps fail).
- Light intensity
Generally speaking, light rays are emitted in different directions and have different intensities. The luminous flux emitted by the light source in a certain direction angle is called light intensity. Unit: Candela (cd).
- Brightness
Brightness refers to the intensity of the reflected light from an object seen by the eye from a certain direction. Unit: Candela/square meter (cd/m2)
- Light color
Light color is actually color temperature. It is roughly divided into three categories: warm colors 3300K, intermediate colors 3300 to 5000K, and daylight colors 5000K.
Because of the difference in the composition of the light spectrum, even if the light color is the same, the color rendering of the lamp may be different.
- Color tolerance
The color of the light emitted by a gas discharge lamp with a strong line spectrum can be regarded as a mixture of three monochromatic lights of red, green and blue in a certain proportion.
In order to evaluate the chromaticity difference of color light, the representation of chromaticity coordinates is introduced, which is the chromaticity diagram published by CIE.
For the chromaticity difference between energy-saving lamps, the national standard stipulates that the chromaticity tolerance of the lamp is within 6SDCM as the chromaticity of the lamp is qualified, and the chromaticity outside of 6SDCM is unqualified.
- Economic Life
Considering both the damage of the bulb and the attenuation of the beam output, the integrated beam output is reduced to a specific number of hours. Unit: hour.
This ratio is 70% for outdoor light sources, and 80% for indoor light sources such as fluorescent lamps.
(To Be Continued)










