History of LEDs
Initial development
LED is short for Light Emitting Diode. LED is also a type of diode, which is a solid-state semiconductor device that can convert electrical energy into light energy. It can directly convert electrical energy into light energy.
In 1955, Rubin Braunstein of the Radio Corporation of America discovered the infrared radiation effect of gallium arsenide (GaAs) and other semiconductor alloys. In 1962, Nick Holonyak Jr of General Electric Company (GE) of the United States developed a red LED for visible light. At that time, it could only be used for the radio indicator light, and the brightness was extremely low.
period of rapid development
After nearly 30 years of development, the world’s first blue light-emitting diode in gallium nitride (GaN) was developed in 1993, laying a solid foundation for three primary colors and making great contributions to the future development of white LEDs. Everyone is very familiar with LED, which can emit red, orange, yellow, green, blue and other colors. However, white light LEDs for lighting were only developed after 2000.
The earliest LED light source made of semiconductor P-N junction light-emitting principle came out in the early 1960s. The material used at that time was GaAsP, which emits red light (λp=wavelength 650nm).
When the driving current is 20mA, the luminous flux is only 1/100 lumen, and the corresponding luminous efficacy is about 0.1 lumen/watt.
In the mid-1970s, the elements In and N were introduced to make LEDs produce green light (λp=wavelength 555nm), yellow light (λp=wavelength 590nm) and orange light (λp=wavelength 610nm), and the luminous efficacy was also increased to 1 lumen/watt .
LED light sources of GaAlAs appeared in the early 1980s, , making the luminous efficacy of red LEDs reach 10 lumens/watt.
In the early 1990s, two new materials, GaAlInP, which emits red and yellow light, and GaInN, which emits green and blue light, were successfully developed, which greatly improved the luminous efficacy of LEDs. In 2000, the luminous efficacy of the LEDs made by the former reached 100 lumens per watt in the red and orange regions (λp=615nm), while the luminous efficacy of the LEDs made by the latter in the green region (λp=530nm) could reach 50 lumens. /watt.
The figure below shows the circuit symbol of an LED light-emitting diode, with the positive pole on the left and the negative pole on the right.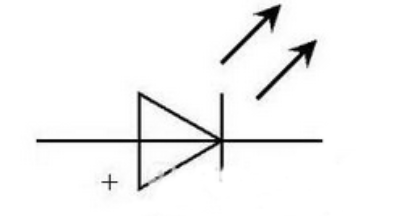
Classification of LEDs
(1) Luminous color
LEDs can be divided into: red, green, blue, yellow, and white according to the luminous color.
White can also be divided into: warm white, neutral white, white, cool white.
The meaning of warm white is: a warmer feeling, a little yellowish, but not yellow, like the sky at dusk. Neutral whites are slightly lighter than warm whites. True white is the color of the noon sun. Cool white is the color of a clear sky with white clouds, a little bluish.
(2) Voltage
LEDs are divided according to voltage levels: yellow and red are generally 1.8-2.2V. White, blue and green colors are generally: 3.0-3.8V.
(3) Color temperature
According to the color temperature grade:
Warm white is: 2700-3500K.
Neutral White: 4000-4500K
Positive white is: 5000-6000K
Cool white is: 7000K
K is the unit of color temperature.
(4) Packaging method
According to the packaging method: In-line LED (DIP), such as: round head LED, straw hat LED, etc.
SMD LED (SMD) such as: 3528, 5050, 5730, etc.
Integrated Package LED (COB).
Flip-Chip LEDs (FLIP-CHIP).
(5) Current
According to the current level: 20mA (0.06W), 30mA (0.1W), 150mA (0.5W), 350mA (1W) and 700mA (3W).
(6) Color rendering index
According to the color rendering index: 60RA, 70RA, 80RA, 85RA, 90RA, 95RA. RA is the unit of color rendering index. The higher the color rendering index, the smaller the distortion of LED light.
90-95RA LEDs are generally used for medical lighting and military lighting and aviation lighting products.
80-85RA LEDs are generally used for high-end commercial lighting.
(7) Power
Divided according to power.
(8) Lighting angle
Divided by lighting angle: 15°, 25°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 120°.
(9) Light color and wavelength band
Divided by luminous color band:
620-625NM for red light RED
590-595NM is yellow light YELLOW
470-475NM for Blu-ray BLUE
520-525NM for green light GREEN
250-265 for low violet light These UV lights can kill details in water
The most lethal is the 285nm wavelength.
365-370NM is medium purple light, which is lethal, please do not look directly.
405-410 is high violet light for currency identification
345-410 for Plant Cultivation
(10) Divided by light intensity
According to the light intensity, it is divided into 100MCD, 200MCD, 300MCD, 500MCD, 800MCD, 1200MCD, 3000MCD-12000MCD, etc.
The unit of light intensity is CD, 1000mcd=1CD.
(11) Divided by the brightness of light
According to the brightness of light, there are 1LM red light, 1-2LM yellow light, 3-5LM green light, 6-7LM white light, 10-20LM white light, 50-55LM white light, 100-120LM single white light, 120-170LM single white light Wait.
The unit of brightness of light is: LM is lumens per watt. The brightness per watt of incandescent lamps is generally 8-10LM, the brightness of energy-saving lamps is generally 60-70LM per watt, and the brightness per watt of LED is generally 80-120LM. Lumen is the maximum brightness per unit area.
(12) Use environment level
According to the level of use environment, it is divided into civil level, medical and commercial lighting level, and automotive lighting level.
The main users of automotive lighting levels are automotive taillights, automotive daytime running lights, automotive headlights, high-mounted brake lights, etc. The requirements for LEDs are quite high, and the temperature of LED chips needs to withstand 130℃-150℃.
When the temperature of the civilian-grade chip is higher than 80℃, serious light attenuation will occur, and the chip may even burn out and fail.
Commercial lighting grade: Commercial lighting grades generally use chips with temperatures >105°C-130°C to package finished LEDs, and most of them use chips from internationally renowned brands to package finished LED particles.
Material for Producing LEDs
What materials are needed to produce white LED semiconductor diodes?
(1) Semiconductor chip
Semiconductor chips are the main material for LED production. Chips are usually relatively small, and the unit is expressed in imperial mil. 1mm=40mil, the luminous flux size of 2835LED 22-24LM commonly used on the market is generally 9 × 20 mil, 9 × 22 mil. 23 – 25 LM chips are generally 9 × 26 mil, and 26lm chips are generally 11 × 28 mil. It is a crystalline chip grown on a sapphire substrate with gallium nitride and sprayed with nitrogen. There are mainly these companies in the world that can produce chips: CREE in the United States, Purui in the United States, OSRAM in Germany, Seoul in South Korea and DOMINANTtm in Malaysia.
(2) Package bracket
The package bracket is the body of the fixed chip, including the pad shell. The packaging bracket has a simple manufacturing process and is mature and stable. The international quality is relatively good, such as CERR and so on.
(3) Phosphor
Phosphors are one of the main materials of white LEDs. White light LED is a white light LED with different color temperature modulated by adding phosphor powder with blue light chip. Phosphors are more expensive, and good phosphors cost about the same as gold.
(4) Packaging glue
Encapsulation glue: It is mainly used to mix phosphors and fix the chip. Good glue, LED light decay is very low.
(5) Gold wire
The main function of the gold wire is to lead out the positive and negative electrodes on the chip and fix them on the pads of the bracket. The gold wire manufacturing process is simple and mature and stable.






