Lighting Arrangement Requirements:
① Ensure the lowest illuminance and make the illuminance of the working surface uniform.
② The direction of the light is appropriate, and there is no glare, shadow and other phenomena.
③ The installation capacity should be as small as possible to reduce investment and annual power consumption,
④ The maintenance work should be convenient and safe.
⑤ The layout is neat and beautiful, and coordinated with the building space.
⑥ Arrangement of general lighting.
There are usually two types, namely uniform arrangement (light arrangement is independent of equipment location) and selective arrangement (light arrangement is related to equipment location). Among them, the uniform arrangement is more beautiful and uniform, so the general lighting is used more.
Evenly arranged lights can be arranged in a square or rectangle or diamond shape as shown.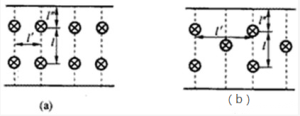
The picture shows the uniform arrangement of lights and lanterns can be arranged in square or rectangle or diamond
Arrangement of emergency lighting
For accident lighting for continued work, the illuminance on the main working surface should be kept as close as possible to 30% to 50% of the original illuminance. The general practice is: if it is a column of lights, it can be arranged alternately with accident lighting and work lighting, or with two work lights. If there are two columns of lights, one of the columns can be selected as emergency lighting, or each column can be arranged alternately with emergency lighting. If there are three columns of lights, you can choose one column for emergency lighting or arrange emergency lighting in two columns next to each other.
- Hanging height of indoor lights
Indoor lighting should not be too high or too low. If it is too high, the illumination on the working surface will be reduced and maintenance will be inconvenient. If it is too low, it is easy to crash and unsafe. On the other hand, glare is generated, which reduces the vision of the human eye.
- Distance between illuminators
When the illuminators are evenly arranged, the ratio of the distance between the illuminators and its calculated height is called the distance-to-height ratio l:h
- Arrangement of outdoor lighting
Generally, spherical lights are installed near the main transformer. Appropriately install floodlights around the power distribution installation yard to illuminate the entire site. The road lighting in the whole factory area is generally arranged in a single row. However, in the entrance avenue and the square, multiple columns of symmetrical or asymmetrical devices can be used.
Illuminance Calculation
When the type of lights and light sources used for lighting in industrial enterprises have been initially determined, it is necessary to calculate the illuminance of each working surface to determine the power and quantity of bulbs, or to verify the illuminance of a certain point where the power has been determined.
1. utilization factor
The utilization factor (represented by K1) refers to the ratio of the luminous flux projected by the illumination light source onto the work surface to the luminous flux emitted by all light sources. It can be used to characterize the degree to which the luminous flux of the light source is effectively utilized.
The formula for calculating the utilization coefficient is:![]()
In the formula, Φ is the total luminous flux projected on the working surface, Φ is the luminous flux emitted by each light, and n is the number of lights.
The size of the utilization factor is related to many factors. The higher the hanging height of the lights and the higher the light efficiency, the higher the utilization factor. The larger the area of the room, the closer the shape is to a square, and the lighter the color of the walls, the higher the utilization factor.
2. Determination of utilization factor
The value of utilization factor can be determined according to the reflection coefficient ρ of walls and ceilings and the room space ratio (illuminated space characteristic) RCR of the room. The value of RCR can be calculated as follows:
In the formula, h is the height of the indoor space (referring to the space height from the opening plane of the light to the working surface), l is the length of the room, and b is the width of the room.
3. Calculate the average illuminance on the work surface
When the length and width of the room, the height of the room space, the light type and the luminous flux are known, the average illuminance can be calculated as follows:
In the formula, K1 is the utilization coefficient, n is the number of lights, Φ is the luminous flux of each light, S is the area of the illuminated working surface (the rectangular room is the product of length and width), and Kj is the dimming compensation coefficient.
During the use of the light, the light efficiency of the light source itself will gradually decrease, the light will also be old and dirty, and the walls and ceiling of the illuminated place may also be contaminated, thus reducing the luminous flux on the working surface. Therefore, when calculating the actual average illuminance on the working surface, a luminaire dimming coefficient Kj less than 1 should be included.
4. Calculation steps using the coefficient method
1) According to the arrangement of lights, determine the height of the room space,
2) Calculate the room space ratio RCR,
3) Determine the reflection coefficient (look up the table),
4) Determine the utilization factor K1 (by RCR value and reflection coefficient),
5) According to the relevant manual or table 10-6, find out the luminous flux Φ of the arranged lights,
6) Find out the dimming coefficient Kj according to the relevant manual or Table 10-5,
7) Calculate the average illuminance and the actual average illuminance.







