Introduction to White LED
With the successful development of 100 lm/W white light LEDs, white light LEDs have taken another step forward in the popularization of display and lighting applications. This article mainly introduces the structure and principle of the new application of white light LED, and its application in life. And under the condition of a current of 20 A and a distance of 50 mm, the brightness was tested with BM27. The test result is that the average brightness is greater than 3,400 cd/m2, and the uniformity exceeds 85%.
LED is the abbreviation of light emitting diode, which is an electric light source made by semiconductor technology. The core part of the LED is a wafer composed of P-type semiconductors and N-type semiconductors. There is a transition layer between the P-type semiconductor and the N-type semiconductor, which is called a P2N junction. During forward conduction, the majority and minority carriers in the semiconductor recombine, and the released energy is emitted in the form of photons or part of it. A large number of photons form a stream of photons, that is, emit light. When the reverse voltage is applied to the P2N junction, it is difficult to inject minority carriers, so it does not emit light.
Due to the different band gap energies of semiconductor materials, LEDs of different semiconductor materials can emit light of different colors.
Advantages of LED Light Source
LED light source has the characteristics of small size, long life, low power consumption, fast response, rich colors, and flat packaging. It is an environmentally friendly and energy-saving cold light source. Due to the above characteristics of LEDs, they are widely used in display and lighting fields.
In 1965, the first commercial LED (red light) came out with an efficiency of only 0.1 lm/W. In 1968, the efficiency of LED made of GaAsP material has reached 1 lm/W, and can emit red, orange, and yellow light.
In the early 1990s, the successful development of two new materials, GaAlInP, which emits red light and yellow light, and GaInN, which emits green and blue light, greatly improved the light efficiency of LEDs. In 1998, the successful development of white LEDs marked the arrival of a revolution in lighting technology.
The latest development of white LED
In December 2006, a white LED with a luminous efficiency of 150 lm/W at a forward current of 20 mA came out. Its luminous efficiency reaches about 1.7 times that of fluorescent lamps and 11.5 times that of incandescent lamps, and even exceeds the high-pressure sodium lamp that is generally believed to have the highest luminous efficiency.
Another new process for manufacturing gallium nitride (GaN)-based and other nitride-based high-quality compound semiconductors is mainly used for blue and white LEDs.
In February 2007, the new LED epitaxy technology basically solved the problem of white light high-power LED luminous efficiency falling with the current increase. The light effect can be increased with the increase of the driving current. A company claims that the use of plastic materials can make the price of white LEDs cheaper. This technology can significantly reduce manufacturing costs, and the brightness of the lighting is better than traditional white LEDs.
In March 2007, an octagonal 2W single chip with 35,000 hours and 96 lm luminous flux was born. It can be directly plugged into 110 V or 220 V AC power supply, no AC/DC converter is needed. In 2008, the luminous efficiency of the chip was increased to 120 lm/W.
At present, the thickness of the LED chip is only 0.4 mm. LED light extraction technology has also made great progress. Therefore, backlight sources with LEDs are gradually used in small displays such as third-generation mobile phones, PDAs, portable DVDs, and digital cameras. In addition, various lights on automobiles, such as front and rear lights, side lights, headlights, interior lights and dashboard displays, will be fully developed and applied.
According to the statistics of Strategies Un2limited, all new cars by 2028 will use LEDs as their headlights.
White LED light
1. The structure and principle of LED lights
The LED lights currently manufactured are mostly small in size. The area of the light-emitting part ranges from 3.81 cm2 (1.5 inches) to 6.0 cm2 (2.4 inches). The structure is divided into five parts: frame, backlight module, flashing circuit, power supply part and switch.
(1) Frame
The frame is used to install and integrate other parts to make it a whole. According to different needs, it can be processed into different geometric shapes, such as rectangles, circles and pentagrams.
(2) Backlight module
The backlight module is the most important part of the LED lamp, which determines the light-emitting area and luminous quality of the card light. The backlight module is composed of an LED lamp, a reflector, a light guide plate, a diffuser, a light shield, an antireflection prism, and a backlight frame.
The LED lamp is the luminous source, and the light guide plate expands the light emitted by several LED lamps to the entire luminous surface. The diffuser plate makes the emitted light more uniform through the principle of diffuse reflection. The antireflection prism can change the angle of the emitted light, focusing more light in the direction of the front viewer. The shading plate is used to control the light-emitting area and the shape of the light-emitting surface.
(3) Flashing circuit
A flashing circuit is usually installed inside the LED lamp, and the light-emitting part of the card lamp is adjusted to emit several different modes of light by controlling the switch. The ordinary flashing circuit can provide three modes: constant light, long interval flashing, and fast flashing.
(4) Power supply part
The operating voltage of the LED is around 3 V. Due to the power-saving features of LEDs, the power supply for the card lights can be button batteries. The lamp powered by a button battery has a compact structure and can be made into a product with a smaller thickness. A removable rechargeable lithium battery can also be used. The advantage of using a rechargeable lithium battery is to save resources. If the card lamp is used frequently, it is more reasonable to use a rechargeable lithium battery.
(5) Switch
Used to connect the circuit and the power supply, adjust the light on, off and light-emitting mode.
2. Brightness test
Use a multi-point luminance meter (BM-7) to test the brightness of LED lights. BM-7 has 4 measurement angles, such as 2°/1°/0.2°/0.1°, etc., which can be switched. The smallest measurement area can reach φ0. 1 mm2. It can measure brightness L, chromaticity X, Y, three color values X, Y, Z, color temperature, response time, contrast, etc. It is widely used in the measurement of LCD, BLU, LCM and other fields, and it is the standard of the LCD industry.
- The 8 cm (1.5 inches) LED light has two white LEDs. Use BM-7 to test the brightness of a lamp with a luminous area of 3. 8 cm2 (1.5 inches). The brightness test adopts the nine-point test method.
3. Data analysis
The calculation formula of uniformity R is: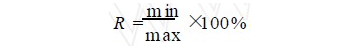
Calculated from the above formula, the uniformity of the effective light-emitting parts of the five groups of backlights are 92%, 86%, 93%, 92%, and 88%, respectively. The maximum uniformity has reached 93%, and the minimum is 86%. All uniformities are above 85%, which shows that the lamp has a very high light source uniformity. Usually, the brightness of more than 200 cd/m2 can meet the application.
In order to compare the brightness of each test point intuitively, the average value of five brightness is taken for each point to make a three-dimensional surface graph. As shown in the figure below, the horizontal axis and the vertical axis of the horizontal plane indicate the position of the measuring point, which is marked with the point number. The vertical numerical axis represents the average value of the brightness of 9 points, and the unit is cd/m2.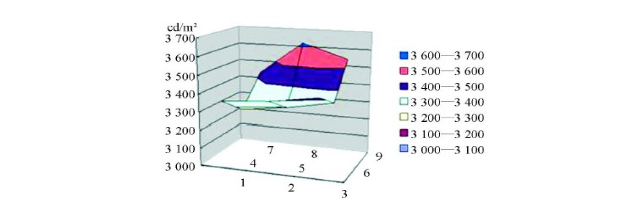
The above data shows that the brightness and uniformity of the card lights are very good.
However, it can be seen from the figure that the edge brightness of the light-emitting surface is high, and the center brightness is low. This point needs to be improved in the future.
4. Application of LED lights
LED lights have many applications in daily life. White LED lights are small in size and environmentally friendly, and are usually integrated in other commodity structures. Translucent cards (such as business cards, labels, holiday cards, etc.) can be attached to the light-emitting part of the lamp. When the light is on, especially in the dark, the content of the card will be highlighted.
In addition to white lights, red, green, and yellow LEDs have been used to make colored lights. The gift box is equipped with this kind of colored light, which can play a decorative role. In addition, because the lamp is equipped with a flashing circuit, the flashing light can attract people’s attention, so LED lights are also used for safety.
Concluding remarks
With the successful development of 150 lm/W white light LEDs, the popularization of white light LEDs in display and lighting applications has taken another step forward. There are also more and more new devices made from white LEDs. The European Union has stated that it will completely replace incandescent lamps with LEDs within two years. The Chinese government has also launched a green lighting project. What is certain is that with the increasing application of white LEDs in automobiles, display backlights, and lighting appliances, the LED era is bound to come soon.