Advantages of LED Lights
The most common one on the market is a non-electrolytic capacitive light engine whose power efficiency is usually only about 85%. The LED lamp is an electroluminescent semiconductor material chip, which is cured on the bracket with silver glue or white glue, and then connects the chip and the circuit board with a silver wire or gold wire. The surrounding is sealed with epoxy resin to protect the inner core wire. Function, finally install the shell, so the LED lamp has good seismic performance. LED can directly emit red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, orange, purple, and white light. LED lights are environmentally friendly, free of mercury, lead and other harmful substances, and can be recycled and reused safely.
The assembly parts of the LED lamp can be easily disassembled and assembled, and can be recycled by others without being recycled by the manufacturer.
No flicker, pure DC work, eliminating the visual fatigue caused by traditional light source flicker. Reduce line loss and no pollution to the power grid. The power factor is ≥0.9, the harmonic distortion is ≤20%, and the EMI conforms to the global index, which reduces the power loss of the power supply line and avoids high-frequency interference and pollution to the power grid.
The effect of high temperature on LED lights
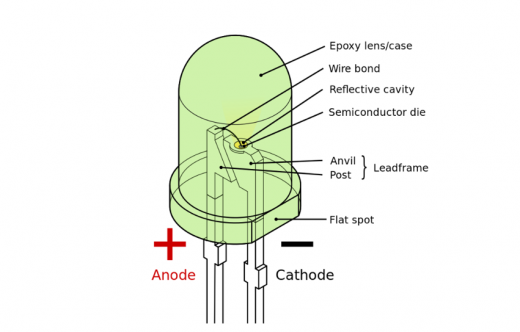
The light emitting diode is a solid-state semiconductor device that can convert electrical energy into visible light. It can directly convert electricity into light. The heart of the LED is a semiconductor chip, one end of the chip is attached to a support, one end is the negative pole, and the other end is connected to the positive pole of the power supply, so that the entire chip is encapsulated by epoxy resin.
This means that 15% of the input power will be converted into heat and added to the aluminum substrate. Assuming that the total input power is 10 watts, the remaining 8.5W will be converted into light output by the LED. Assuming that the luminous efficiency of the LED itself is 40%, that is, only 3.4 W of power is converted into useful light, and 5.1 W of power is converted into heat. It turned out that as long as the aluminum substrate dissipates the 5.1W of heat, and now it is necessary to increase the power supply by 15%, that is, the heat of 1.5W, then a total of 6.6W needs to be dissipated, an increase of 29.4% of the heat, which is close to 30%.
However, the thermal resistance of the aluminum substrate remains the same. The increase in power means the temperature rises, and the temperature of the aluminum substrate rises, which means that the ambient temperature of the LED on the same aluminum substrate rises, and the junction temperature rises, resulting in The luminous efficiency drops.
During the welding process of led lamp beads, the temperature of the welding iron tip should not exceed 300℃, the welding time should not exceed 3 seconds, and the welding position should be at least 2 mm away from the colloid.
Dip soldering: the highest temperature of dip soldering is 260℃, the dip soldering time is no more than 5 seconds, and the dip soldering position is at least 2 mm away from the colloid.
Pin formation mode: It must be separated from the gel by 2 mm to bend the bracket. The stent molding must be done with a fixing device or by a professional. The bracket forming must be completed before welding. The molding of the bracket should ensure that the pins and spacing are consistent with the circuit board.
Installation method of LED light:
Pay attention to the arrangement of various equipment outside the line to prevent incorrect polarity installation. The LED lamp is an electroluminescent semiconductor material chip, which is cured on the bracket with silver glue or white glue, and then connects the chip and the circuit board with a silver wire or gold wire. The surrounding is sealed with epoxy resin to protect the inner core wire. Function, finally install the shell, so the LED lamp has good seismic performance. LED can directly emit red, yellow, blue, green, cyan, orange, purple, and white light. The device should not be too close to the heating element, and its working conditions should not exceed its prescribed limits.
Please make sure not to install the LED indicator when the pins are deformed. The LED lamp technology is advancing with each passing day, its luminous efficiency is making amazing breakthroughs, and the price is constantly decreasing. The era of white LEDs entering the home is rapidly approaching. Impact resistance, strong lightning resistance, no ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation. There is no filament and glass shell, there is no broken problem of traditional lamp tube, no harm to human body, no radiation.
When deciding to install in the hole, calculate the size and tolerance of the panel and the distance between the holes on the circuit board so that the bracket will not bear excessive pressure. When installing the LED light, it is recommended to use a guide sleeve to locate the indicator light. Before the welding temperature returns to normal, the LED light must be protected from any vibration or external force.
The difference between cold light source and hot light source
Heat source:
A light source excited by thermal energy, such as an incandescent lamp, emits light with thermal radiation at a temperature of 3,000-4,000K. Incandescent lamps have 80-90% of the energy converted into heat energy, and about 10% of the energy is converted into light energy. Therefore, the luminous efficiency is low. We do not define it as a cold light source or a hot light source based on the temperature of the lamp housing. The temperature around the lamp can only judge the heat dissipation measures of the lamp.
Cold light:
The cold light source is a light source excited by chemical energy, electrical energy, and biological energy (fireflies, neon lights, LEDs, etc.). It has very good optical and variable flicker characteristics. When an object emits light, its temperature is not higher than the ambient temperature. This type of light emission is called a cold light source. For example, LEDs use electron-hole pairs to recombine light.
Strictly speaking, LED light-emitting diodes are electroluminescence and also generate heat, but they are lower than light sources such as incandescent lamps. The LED electro-optical conversion efficiency is about 30%, of which the internal quantum efficiency is about 70% (close to the theoretical limit), and the external quantum efficiency is about 50% (this is only experimental data, not an accurate value).
the difference:
The cold light source we are talking about does not mean that no heat is generated during the light-emitting process, but that the way of light-emitting is not converted from thermal energy to light energy. Incandescent lamp is a process that typically converts electrical energy into heat energy, and then heat energy into light energy. The heat loss is high and the luminous efficiency is low. According to the current development trend of LED white light, the era of cold light sources replacing hot light sources is not far away. Therefore, we can regard LEDs as cold light sources.
Influence of heat on the performance and structure of LED
- LED is a temperature sensitive device. When the temperature changes, the performance and packaging structure of LED will be affected, which will affect the reliability of LED.
- The heat is concentrated in the small size LED chip. If there is no effective heat emission, the chip temperature will rise, resulting in the non-uniform distribution of thermal stress, and the luminous efficiency and phosphor lasing efficiency of the chip will decrease.
- When the temperature of the LED chip exceeds a certain value, the failure rate of the device increases exponentially. The statistical data show that the reliability decreases by 10% for every 2 ℃ rise in the temperature of the module.
- When multiple LEDs are densely arranged to form a white lighting system, the problem of heat dissipation is more serious.
- Heat will affect the efficiency of LED driver, damage the life of magnetic components and output capacitors, and reduce the reliability of LED driver (Generally, the working temperature of semiconductor components should be controlled at less than 80 ℃ ).
- A typical LED is encapsulated by an optically transparent epoxy resin. When the temperature rises to the glass transition temperature Tg of the epoxy resin, the epoxy resin is converted from a rigid material to an elastic material, and the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) will change greatly.
During the temperature change of the encapsulation resin, the expansion and shrinkage will increase, which will lead to the increase of the displacement of the bonding point of the gold wire (or aluminum wire), and the premature fatigue and damage of the gold wire (or aluminum wire), In order to avoid the sudden failure of LED, the LED node temperature should always be kept below Tg of the packaging resin.
The influence of heat on the material of LED light channel:
Accelerate the aging of the material in the light channel
Reduce the transmittance of channel material
Changing the refractive index of the material in the light channel, affects the spatial distribution of light
When it is serious, the optical channel structure will be changed
Causes expansion or contraction of the packaging material
The deformation stress caused by the expansion or contraction of the packaging material increases the displacement of the ohm contact / solid crystal interface, resulting in open circuit and sudden failure of LED.
At present, due to the low output beam of a single LED, a large number of LED components will be needed in a module for general lighting to achieve the required illumination, but the photoelectric conversion efficiency of LED is poor, only about 15% to 20% of the electric energy is converted into light output, and the rest is converted into heat energy. Therefore, when a large number of LEDs are used in a module, this extremely poor conversion efficiency will bring great hidden dangers to the heat dissipation of the LEDs.





